It’s not enough to simply run marketing campaigns and hope for the best. You need to know if your strategies are truly working, and more importantly, how they can be improved. That’s where marketing audits come into play. Did you know that companies conducting regular marketing audits often discover critical insights that lead to significant performance boosts?
It’s a practice employed by top brands to maintain their competitive edge, ensuring that every marketing dollar is spent wisely. Marketing audits offer a structured way to assess the effectiveness of your marketing efforts, identifying what’s working, what isn’t, and where there’s room for improvement.
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a clear understanding of how to conduct a thorough marketing audit, empowering you to refine your strategy and drive better results.
- Understand the Purpose of a Marketing Audit: A marketing audit is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of your current marketing efforts and identifying areas for improvement.
- Identify Key Metrics and KPIs: Focus on the most relevant metrics and KPIs to assess the success of your marketing strategies, ensuring they align with your business goals.
- Evaluate All Marketing Channels: Conduct a comprehensive review of all marketing channels, including digital, social media, and traditional channels, to ensure they are contributing effectively to your objectives.
- Analyse Competitor Strategies: Gain insights from competitor strategies by comparing their marketing approaches with yours, helping you identify opportunities and threats.
- Implement Continuous Improvement: Use the findings from your marketing audit to refine and enhance your marketing strategies continuously, ensuring sustained growth and competitiveness.
What is the purpose of conducting a marketing audit for my brand?
Bruce Clark, author of The Marketing Audit and Organisational Performance, defines a marketing audit as a “comprehensive, periodic, systematic, and independent examination of a brand’s marketing efforts.” By conducting a marketing audit, brands can identify their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and any looming issues within their current marketing programme. This enables them to adjust the status quo and accelerate marketing performance in the long term.
What Matters Most?
In our work, a successful marketing audit often hinges on reassessing market segmentation to ensure it aligns with evolving customer needs. Clients typically discover that a failure to adapt to these changes can lead to misaligned strategies and missed opportunities. Additionally, consistently auditing the customer journey can reveal gaps where brand promises are not fully realised, often a crucial factor in sustaining customer loyalty.Get In Touch
Benefits of a Marketing Audit
A marketing audit can significantly enhance a brand’s performance in several ways:
- Identify Areas of Improvement: Marketing audits enable brands to measure current performance against targets across all lines of marketing activity. This process can immediately highlight high-performing (and underutilised) activities, as well as those that are not working.
- Uncover Inefficiencies in the Marketing Strategy: By discovering inefficiencies across data, tooling, and processes in all marketing activities, brands can forensically examine their operational approach. This helps identify opportunities to streamline and optimise team performance.
- Identify Areas Where Brands Can Excel: A marketing audit helps brands realign their marketing activities with those delivering the highest results. This alignment makes it easier for them to achieve targets.
- Set Actionable Items to Move Forward: The ultimate objective of a marketing audit is to build a roadmap detailing and scheduling how the marketing team will optimise their current marketing mix, tooling, and operations. This is crucial for putting insights into action.
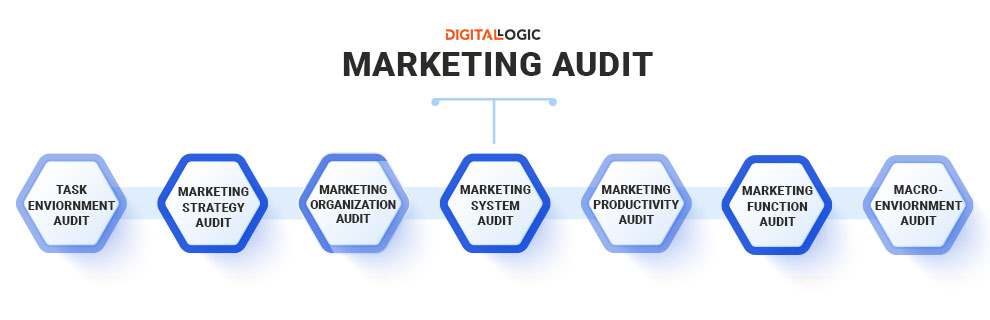
Characteristics of a Marketing Audit
A thorough marketing audit is divided into several key components, each vital to understanding and enhancing marketing productivity:
- Internal Marketing Audit: Evaluates the structure of the marketing team and how various responsibilities are divided. It also reviews the core content and messaging of a brand, analysing and evaluating the product or service, the brand, promotions, and pricing strategy. This includes competitor analysis and performance evaluation of marketing channels like social media, blogs, and newsletters.
- External Marketing Environment: Reviews external factors influencing marketing performance. This includes task environment audits, which assess market conditions and shifts in customer attitudes, and macro-environment audits, which evaluate changes in regulations, geo-politics, economics, demographics, and cultural aspects.
Current Marketing Strategy: Evaluates the overall marketing strategy and productivity to see which campaigns, processes, and tactics are working. This involves marketing strategy audits to assess the business from a macro perspective and marketing productivity audits to review the effectiveness of every channel and campaign.

What are the key components of a marketing audit?
A comprehensive marketing audit is segmented into three crucial areas. Performing an in-depth analysis and evaluation across these segments can significantly enhance marketing performance.
Internal Marketing Audit
- Marketing Organisation Audit: Brands should assess the structure of their marketing team and the division of responsibilities. This structure must align with best practices and the brand’s business model.
- Marketing Function Audit: This audit focuses on reviewing a brand’s core content and messaging. It involves analysing and evaluating the product or service, the brand itself, promotions, and pricing strategy. This also includes assessing the product’s Unique Selling Proposition (USP) against competitors, incorporating competitor analysis as part of the process.
- Marketing Channels Audit: It is essential to evaluate the performance of a brand’s marketing channels. This involves analysing where the business communicates with potential or existing customers and measuring the performance of these channels against competitors and the brand’s goals and KPIs. Channels typically audited include social media, landing pages, blogs, and newsletters. Depending on the business, this can also extend to offline channels.
External Marketing Environment
After reviewing internal factors, brands should consider external influences affecting their marketing performance.
- Task Environment Audit: A brand must review the current state of its market, considering the specific industry it operates in. Understanding shifts in customer attitudes, outlooks, and needs is crucial for maintaining relevance and avoiding disruption.
- Macro-environment Audit: By evaluating changes in the macro-market, brands can account for shifts in regulation, geopolitics, economics, demographics, and cultural aspects that may impact marketing performance.
Current Marketing Strategy
The third pillar of a marketing audit involves evaluating the current marketing strategy and productivity to identify effective campaigns, processes, and tactics.
- Marketing Strategy Audit: Brands should examine their business from a macro perspective. Key questions include: Are they targeting the right audience? Is the product priced appropriately? Do their promotions yield a favourable return on investment? Do competitors offer similar but cheaper products? Is the brand perceived as outdated compared to new market entrants?
- Marketing Productivity Audit: This audit reviews the effectiveness of every marketing channel and campaign. By evaluating the cost of each marketing asset, brands can determine how to adjust financial and staff resources to maximise productivity and return on investment. This thorough marketing productivity audit ensures that resources are utilised effectively to achieve the best possible outcomes.
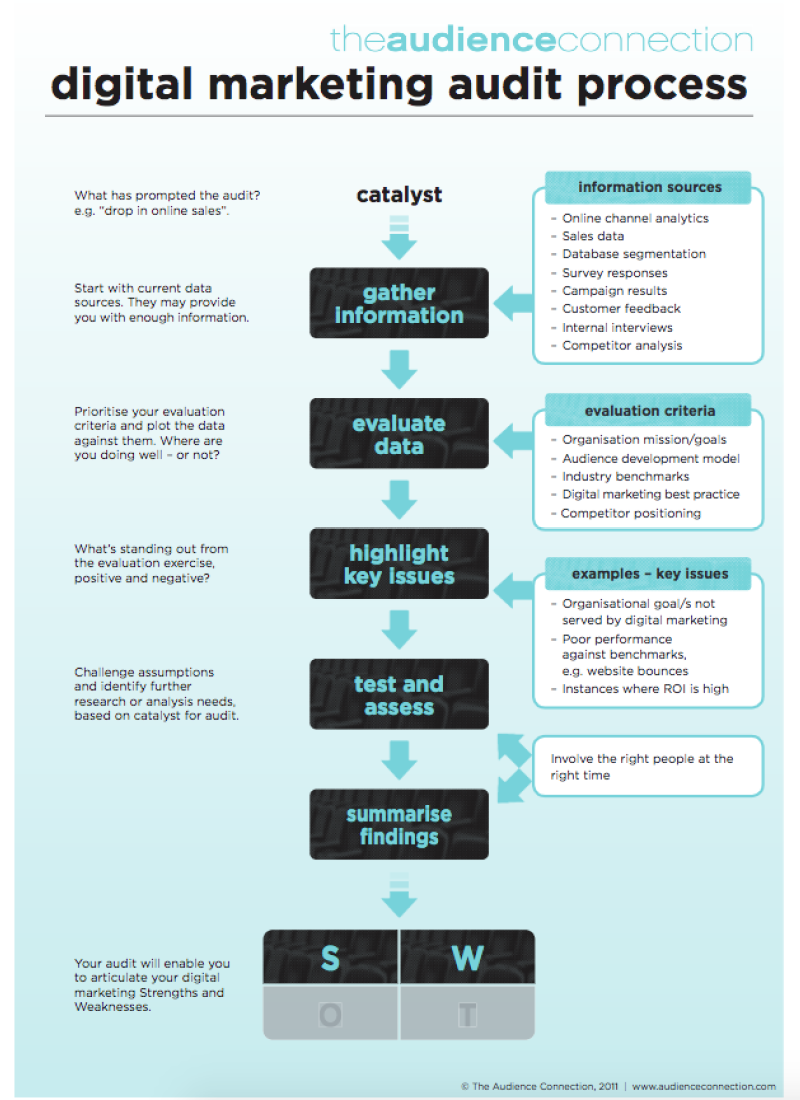
How do I perform a digital marketing audit effectively?
Having covered the overarching marketing audit, let’s delve into a more digital-centric approach. A digital marketing audit focuses on a brand’s digital competencies and the effectiveness of its digital presence. This type of audit ensures that from the outset, a brand makes the right decisions in its digital investments and strategy. In a digital marketing audit, there are several key areas to analyse.
1. Online Benchmarking and Competitor Set Analysis
By benchmarking its performance against that of its competitors, a brand can identify areas where it is underperforming and uncover the weaknesses in competitors’ strategies. Brands should benchmark all their digital KPIs against the competitor set. From these benchmark results, brands can identify opportunities to strengthen their existing approach and ensure long-term success.
2. Digital Channel Audit
Auditing each individual digital channel helps brands identify low-hanging fruit and channels that consume a disproportionate share of the budget relative to their performance. Digital channel audits should delve deeply into platform specifics and analyse best practices against the current approach. For instance, is the brand using the right hashtags and sharing stories on Instagram? Are blog posts tagged to get featured as search snippets on Google?
3. Audit Digital Content
Auditing digital content involves more than just assessing the quality of videos or copy. Conducting a deep dive into content topics, channel formats, and distribution strategies enables a brand to optimise its current approach and drive significant improvements in content performance. Key considerations include: Does the content provide value to the target customers? Is it formatted correctly for platforms like Facebook? How is the content distributed? Does it align with the brand’s values and aesthetics? Is the content mix diverse, including videos, photos, social posts, infographics, and emails?
4. Tooling Audit
A tooling audit evaluates a brand’s current marketing technology stack and the team’s approach to using this technology. Based on the brand’s market, target customers, and marketing strategy, the audit assesses the current tools and their usage, and builds a roadmap to optimise the marketing tech stack and streamline tool usage to enhance marketing performance.
5. SEO Audit
An SEO audit is one of the most common audits due to its pivotal role in driving website traffic. However, achieving success with SEO can be challenging without a solid foundation. There are different types of SEO audits, each focusing on distinct areas:
- Technical SEO Audit: This focuses on the technical makeup of the website, ensuring search engines can crawl and index the content effectively.
- Off-Page (Link) Audit: This examines the websites that link back to yours. Originally used to detect Google penalties, backlink audits now help identify opportunities to grow a backlink profile.
- Local SEO Audit: Focused on businesses aiming to rank for local-themed searches and appear in Google’s Map results.
- Content Audit: Although covered in more detail elsewhere, an SEO content audit often involves optimising content with focus keywords as part of a technical audit.
When requesting an SEO audit, it is assumed that the client has some level of understanding. If uncertain about the most appropriate type, it is advisable to provide insight into business goals and let the consultant determine the audit’s focus.
Our Tactical Recommendations
We’ve found that the most impactful audits often begin with a deep dive into content performance, allowing clients to identify which pieces truly contribute to lead generation and conversion. Clients often discover that even minor adjustments to content can yield significant improvements in engagement. Moreover, regularly auditing for conversion rate optimisation on key landing pages typically uncovers simple yet effective changes that can dramatically enhance performance. Lastly, assessing the efficiency of the marketing funnel by identifying drop-off points offers actionable insights into where resources should be focused to maximise ROI, ensuring no opportunities are missed.Get In Touch
Building Blocks of a Best Practice Digital Marketing Audit
A robust digital marketing audit incorporates a variety of analytical methodologies and approaches to provide a comprehensive evaluation. Here are the essential elements:
Quantitative Analysis
Quantitative analysis forms the core of any digital marketing audit. By leveraging performance metrics from marketing analytics, brands can pinpoint what is effective and what requires improvement. Key metrics to analyse include Google Analytics data, PPC ads reports, social media metrics, and CRM data reports. This process is fundamental in understanding the quantitative characteristics of marketing audit.
Qualitative Analysis
Performing a qualitative analysis involves evaluating the quality of a brand’s digital marketing initiatives. This includes assessing aspects such as site layout, imagery, calls to action, video content, user experience, brand messaging, and email design. By scoring these elements against best practice standards and competitor benchmarks, brands can identify opportunities to optimise and enhance their digital marketing performance.
Website Crawl
A website crawl is crucial for identifying any malfunctioning parts of a website. Issues to look for include missing title tags, slow site load times, broken links, duplicate content, technical errors, and missing H1 and page title tags. Addressing these issues can significantly improve site performance and user experience.
Competitive Analysis
Competitive analysis involves gathering intelligence on the strengths and weaknesses of competitors’ digital strategies. This information allows a brand to develop a highly competitive marketing strategy that can outperform competitors in the market. Understanding the competitive landscape is a vital aspect of the characteristics of marketing audit.
Channel-Specific Tactics
Evaluating current tactics against the latest features and functionalities available on each platform ensures that a brand maximises the potential of its channels. A set of recommended tactics should accompany the digital marketing audit to ensure that the brand uses the most up-to-date strategies.
Recommendations and Strategy
A comprehensive set of recommendations should be provided as part of the digital marketing audit. This should include a strategic roadmap that transforms these recommendations into actionable projects. The goal is to empower the marketing team to optimise their current approach effectively.
Tools for a Digital Marketing Audit
Several tools and frameworks are available to perform digital audits for clients. Some of the most effective tools include:
- SEMrush: A versatile tool that provides insights into search performance. It helps brands evaluate their performance, analyse competitors, and identify the right keywords to drive target customers to their website.
- Google Analytics: Offers a plethora of metrics to understand digital marketing performance. This includes bounce rates, user flow, device categories, demographics, referral traffic, content drill-downs, and identifying the most popular topics.
- Social Media Networks: Platforms like Facebook Page Insights help brands understand who is engaging with their page and the impact of their social media efforts.
Digital Marketing Audit Checklist to Steal
A thorough digital marketing audit ensures that every aspect of your online presence is optimised for performance and efficiency. Here’s a detailed checklist to guide you through the process.
Digital Marketing Audit Checklist
Google Search Console
-
Check for crawl errors and fix them.
-
Review search analytics for performance insights.
-
Submit your XML sitemap to ensure all pages are indexed.
Robots.txt File
-
Ensure your robots.txt file is correctly configured.
-
Verify that important pages are not accidentally blocked.
URL Structure
-
Check for clean, SEO-friendly URLs.
-
Ensure consistency and use of keywords in URLs.
Breadcrumb Menu
-
Implement and optimise breadcrumb navigation.
-
Ensure it reflects the site structure accurately.
XML Sitemap
-
Verify the sitemap includes all relevant pages.
-
Regularly update the sitemap with new content.
HTTPS
-
Ensure your site uses HTTPS for security.
-
Fix any mixed content issues.
Website Speed
-
Analyse and improve page load times.
-
Utilise tools like Google PageSpeed Insights.
Mobile-Friendliness
-
Ensure your site is fully responsive.
-
Check for mobile usability issues using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test.
Titles and Descriptions
-
Optimise titles and meta descriptions for keywords.
-
Ensure they are unique and compelling.
Headings and Text Formatting
-
Use H1 tags for main titles and H2/H3 for subheadings.
-
Ensure proper text formatting for readability.
Content
-
Check for high-quality, relevant content.
-
Ensure content is aligned with your brand’s message and values.
Internal Linking
-
Verify the effectiveness of internal links.
-
Ensure they enhance navigation and SEO.
Image SEO
-
Optimise images with appropriate alt text.
-
Ensure images are compressed for faster load times.
Broken Links
-
Identify and fix broken links.
-
Use tools like Screaming Frog to find broken links.
Incoming Links
-
Analyse your backlink profile for quality.
-
Identify and disavow any harmful links.
Domain Authority
-
Monitor your domain authority.
-
Work on strategies to improve it, like quality content and backlinks.
Competitors’ Links
-
Review and compare your competitors’ backlinks.
-
Identify opportunities for your own link-building strategy.
Social Media Profiles
-
Check the accuracy and completeness of your profiles.
-
Ensure branding is consistent across all platforms.
Social Media Followers
-
Monitor the number of followers on each platform.
-
Engage actively with your audience.
Social Media Comments
-
Respond promptly to comments and messages.
-
Foster community engagement.
Social Media Handles
-
Ensure consistency of social media handles.
-
Update any outdated information.
Brand Mentions
-
Search for mentions of your brand on Google.
-
Address any negative reviews or feedback.
Website Design
-
Check for a modern, user-friendly design.
-
Ensure it aligns with your brand’s identity.
Core Web Vitals
-
Analyse and optimise core web vitals metrics.
-
Focus on LCP (Largest Contentful Paint), FID (First Input Delay), and CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift).
Conversion Tracking
-
Ensure conversion tracking is enabled.
-
Analyse conversion data for insights.
Important KPIs
-
Regularly review and analyse your KPIs.
-
Adjust strategies based on performance data.
Budget
-
Check your marketing budget allocation.
-
Ensure funds are being utilised effectively.
Ads
-
Review the performance of your ad campaigns.
-
Optimise ad spend and targeting.
Best-Performing Content
-
Identify and leverage your top-performing content.
-
Replicate successful strategies.
Content Review
-
Find pages to remove, consolidate, or update.
-
Ensure content remains current and relevant.
-
Develop a comprehensive content marketing plan.
-
Align content strategy with business goals.
Email Subscribers
-
Monitor the growth of your email subscriber list.
-
Implement strategies to increase subscriptions.
Email Deliverability
-
Check email deliverability rates.
-
Address any issues affecting delivery.
Email Open and Click-Through Rates
-
Analyse email open and click-through rates.
-
Optimise email campaigns for better engagement.
Email Design
-
Ensure email designs are appealing and mobile-friendly.
-
Align designs with your brand’s visual identity.
Email List Hygiene
-
Regularly clean your email list.
- Remove inactive subscribers to maintain list quality.









