With the rapid evolution of consumer behaviours and the increasing demand for personalised experiences, understanding and applying the 4 Ps—Product, Price, Place, and Promotion—has never been more crucial. This guide will take you through the essential steps of defining and refining your market segments, ensuring your strategies not only meet but anticipate customer needs. By the end of this guide, you’ll have actionable insights into identifying market gaps, leveraging data-driven decisions, and differentiating between customer and market segmentation.
- Align the 4 Ps with Market Segmentation: Ensure your product, price, place, and promotion strategies are deeply integrated with your market segmentation to meet and exceed customer expectations.
- Product Development: Focus on developing products that fill a specific gap in the market or offer a unique experience, ensuring they resonate strongly with your target segments.
- Pricing Strategy: Set prices that reflect your target market’s willingness to pay, balancing accessibility with profitability.
- Distribution Channels: Choose distribution channels that match your audience’s purchasing habits, ensuring your product is available where and when they need it most.
- Targeted Promotions: Develop promotional strategies that are tailored to each segment’s preferences and behaviours, enhancing engagement and conversion rates.
- Define and Segment Your Market: Use detailed criteria to define market segments, ensuring homogeneity within segments and clear differentiation between them.
- Identify and Exploit Market Gaps: Continuously analyse market data to uncover new opportunities and refine your segmentation strategy.
- Differentiate Between Customer and Market Segmentation: Understand the distinct roles of customer and market segmentation in targeting both existing clients and potential customers effectively.
What Are the 4 Ps of Market Segmentation?
The 4 Ps of marketing—Product, Price, Place, and Promotion—are interdependent components that together form the cornerstone of any strategic marketing plan. Each element is equally critical, contributing to a cohesive strategy that aligns with your customer market segmentation approach.
Product
The product represents the goods or services you are offering to your target audience. Successful products typically fill a gap in the market or deliver a unique experience that drives demand. For instance, the original iPhone addressed the need for an integrated device combining phone functionality with an iPod, while the Chia Pet offered a quirky, memorable experience that captured consumer attention.
When developing your product, it’s essential to consider the specific needs of your target market. Key questions to guide this process include:
- What exactly is your product, and what does it offer?
- Does your product address an unmet need or provide a novel experience?
- Who precisely is your product’s target audience?
- In what ways does your product differ from competitors’ offerings?
Price
Price is the monetary value assigned to your product or service. Establishing the right price is crucial as it must be accessible to your target market while also meeting your business objectives. Pricing has a profound impact on your market segmentation strategy. If set too high, it may alienate potential customers; if too low, it could signal inferior quality and erode profit margins.
To determine an optimal price point, a thorough understanding of your target audience’s purchasing power and perceptions is necessary. Consider these questions:
- What is the price range for competing products in your market?
- What are the financial capabilities of your target audience?
- At what price would your product be considered too expensive or too cheap?
- What pricing aligns with both your market and business goals?
Place
Place refers to the channels and locations where your product is available to your customers. Selecting the right distribution channels is pivotal in ensuring that your product reaches the intended audience. If your product is not accessible in the places your target market frequents, whether online or offline, your sales goals may not be met.
For example, if you have designed an athletic shoe aimed at athletes aged 20 to 35, placing it in sports shops and advertising it in sports publications would be more effective than selling it in general footwear stores. Your focus should be on selecting places that align with your market segmentation efforts.
Consider these questions to identify the best places for distribution:
- Where will your product be sold?
- Where does your target audience typically shop?
- Which distribution channels will most effectively reach your target market?
Promotion
Promotion encompasses the various methods used to communicate the benefits of your product to your target audience. A well-crafted promotional strategy is essential to ensure that your product is noticed and resonates with your market segments. Traditional promotional methods such as word of mouth, print advertisements, and television commercials remain relevant, but the digital age offers additional channels like content marketing, email campaigns, and social media marketing.
To refine your promotional strategy, consider these questions:
- When is the optimal time to engage your target audience?
- Which marketing channels are most effective for reaching your specific market segments?
- What types of advertising will most persuasively communicate your product’s value to your target audience?
By understanding and strategically applying the 4 Ps within the context of your market segmentation, you can create a marketing plan that not only reaches but resonates with your target customers, ultimately driving growth and success.
What Matters Most?
Businesses often overlook the potential of light buyers; by focusing efforts here, you can significantly enhance market share. It’s essential to align your segmentation strategy with brand equity, ensuring that your messaging resonates deeply with each segment’s values. Regularly reassessing your market segments allows you to adapt to the fast-evolving consumer landscape, ensuring you remain relevant.Get In Touch
Customer Market Segmentation Best Practices
Market segmentation is far from a one-size-fits-all approach. Each business needs to carefully consider the unique variables that define its customer base. Selecting the right segmentation strategy can be pivotal to your marketing efforts. Below, we explore five primary types of market segmentation, each offering distinct insights and advantages.
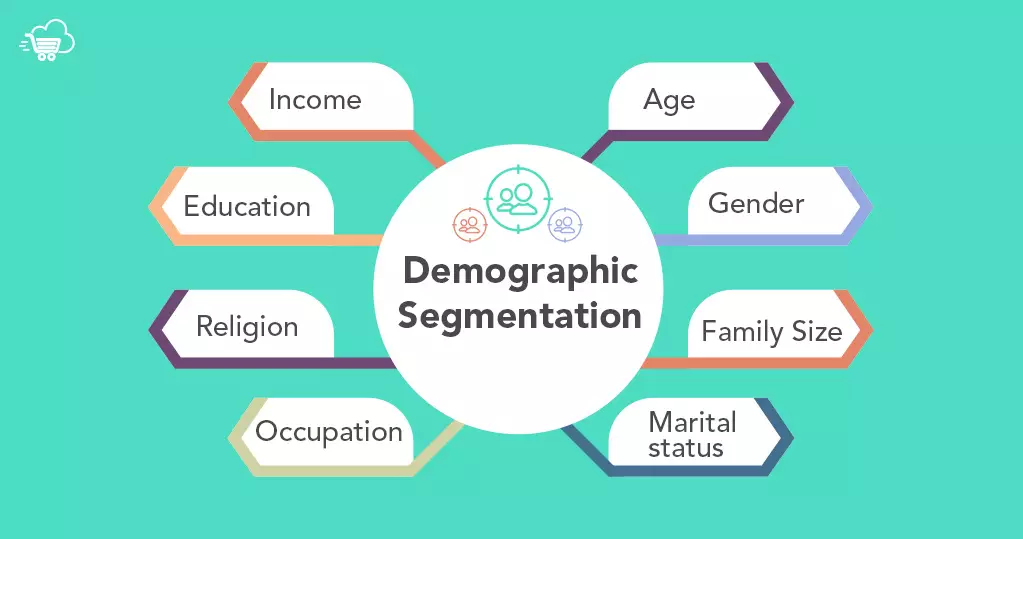
Demographic Segmentation
Demographic segmentation is arguably the most widely used form of customer market segmentation, focusing on characteristics such as age, gender, income, education level, and marital status. It’s popular because demographic data is both accessible and easy to interpret. For instance, a cosmetics brand might develop a specific anti-ageing product line aimed at older consumers, while a luxury car brand may target high-income individuals.
By understanding these demographic variables, businesses can tailor their offerings more effectively, ensuring the product aligns with the specific needs and preferences of each segment within the market.
Geographic Segmentation
Geographic segmentation divides a market based on location, whether that be countries, regions, cities, or even neighbourhoods. This strategy is particularly valuable for businesses whose offerings are impacted by location-specific factors such as climate, local culture, or regional regulations. For example, a clothing company might promote heavy winter coats in colder areas while focusing on lighter garments, like swimwear, in coastal regions.
The ability to tailor your marketing mix based on geographic data ensures that your product or service resonates with customers in distinct locations, aligning your offering with their environmental and cultural needs.
Psychographic/Attitudinal Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation dives deeper than surface-level demographics, investigating the psychological drivers of consumer behaviour, including values, lifestyle, attitudes, and interests. This method is more nuanced but highly effective for brands that need to connect with their audience on a deeper level. For example, a fitness brand targeting customers who are highly health-conscious and committed to regular exercise can use psychographic segmentation to tailor its messaging and product features more closely to this audience.
Attitudinal segmentation can be complex, often requiring advanced techniques such as pairing attitudinal data with clustering algorithms like CCEA, which helps to group customers by shared mindsets, enhancing the precision of your customer market segmentation strategy.
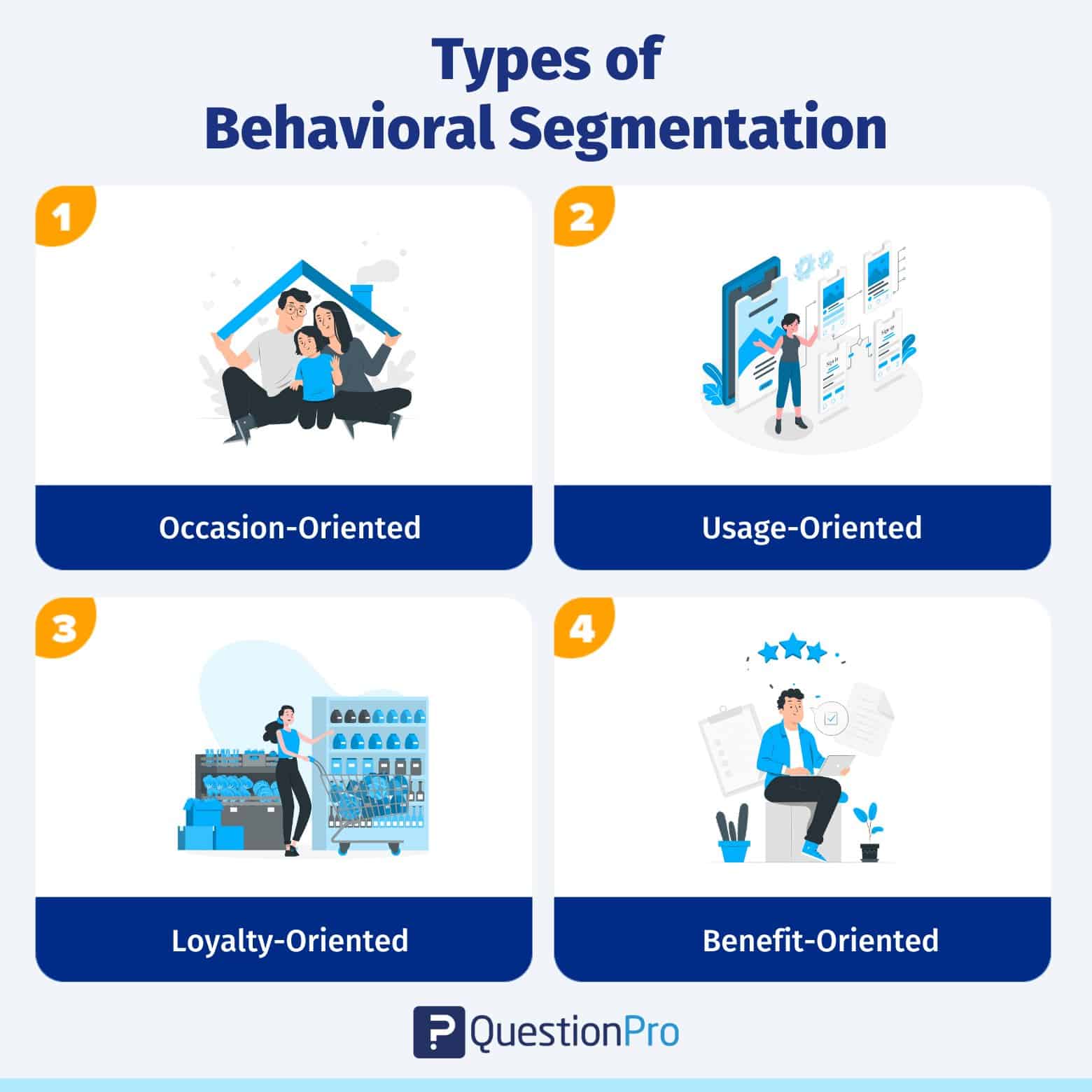
Behavioural Segmentation
Behavioural segmentation centres on the actions customers take, from purchasing habits to brand loyalty and how frequently they use a product. This form of segmentation allows businesses to adjust their strategies based on real-world customer behaviours. For instance, a streaming platform might introduce exclusive offers for users who binge-watch content regularly, enhancing engagement and reducing churn rates.
By aligning your marketing efforts with behavioural patterns, you can create more effective campaigns that meet customers where they are in their journey, increasing retention and long-term loyalty.
Needs-Based Segmentation
Needs-based segmentation identifies and categorises customers according to their specific needs and preferences concerning product features and price sensitivity. This method ensures that your offerings are tailored to those who have particular desires or constraints. Tools such as MaxDiff (best-worst scaling) and conjoint analysis (CBC) are particularly effective for assessing these needs. Additionally, the Latent Class MNL method, widely utilised by Sawtooth Software, helps businesses segment customers into distinct groups based on their preferences and price sensitivity, ensuring maximised differentiation between segments.
With needs-based segmentation, businesses can ensure that their products and marketing messages are not only targeted but also deeply relevant to the specific desires of each customer group.
Market Segmentation Strategy
Understanding your target market is crucial to selling your products or services effectively. However, crafting a well-thought-out market segmentation strategy is essential. This plan helps you identify and target the right segment of the market that aligns with your business objectives.
Below are five key steps to developing a successful customer market segmentation strategy.
1. Define the Market
Defining your market is the first step in uncovering your brand’s niche within a broader audience. This involves ensuring your product or service delivers on the value it promises to your target customers. In this stage, you’ll identify critical factors such as:
- Competitors within similar industries
- Geographic areas where your product or service is relevant
- Key traits of potential customers
This foundational process is crucial for setting clear market boundaries. By doing so, you create a framework upon which the rest of your customer market segmentation strategy will be built.
2. Segment the Market
Once your market is clearly defined, the next step is to divide it into distinct customer segments. This is where you apply the various types of market segmentation. Key steps in this process include:
- Identifying relevant segmentation criteria, such as age, income, or purchasing behaviours
- Grouping customers into clusters with similar traits
- Ensuring homogeneity within each segment to make them meaningful and distinguishable from other groups
- Evaluating the potential growth and alignment of each segment with your business objectives
An effective segmentation process allows you to target your marketing efforts more precisely. By focusing on the right customer market segmentation, you can create tailored marketing messages that resonate with your audience, ultimately reducing wasted resources and maximising impact.
For eCommerce businesses, segmentation tools like Omnisend can enhance personalisation, improve targeting, and drive conversions.
Source: McKinsey
3. Understand the Market
A deep understanding of the market is vital to ensuring the effectiveness of your segmentation strategy. This means thoroughly exploring your potential customers’ needs, pain points, and motivations. To achieve this, follow these steps:
- Gather insights through surveys or focus groups to better understand purchasing behaviours
- Identify common patterns and trends within the data
- Determine which communication methods and promotional tactics work best for each segment
- Research competitors to uncover gaps in the market where your business can capitalise
Since market dynamics are constantly changing, this analysis should be an ongoing process. Customer preferences shift over time, so your market understanding must evolve accordingly to maintain relevance and competitive advantage.
4. Create Customer Segments
With your insights in hand, the next step is to build clearly defined customer segments. This involves converting raw data into actionable groups that can drive your marketing strategies. Consider the following when creating your customer segments:
- Develop comprehensive profiles for each group, capturing critical attributes and behaviours
- Focus on high-value segments that align with your business goals and offer the greatest revenue potential
- Look for overlaps between different segments to ensure you don’t miss opportunities to reach diverse customers with similar needs
The goal here is to translate your customer market segmentation into practical strategies that enhance the customer experience and improve business outcomes.
A robust market segmentation strategy enables you to target your ideal customers with precision and efficiency. By defining your market, segmenting it effectively, understanding your audience, and building well-constructed customer profiles, you ensure your marketing efforts resonate with the right people and drive long-term success.
How Does Long Tail Theory Affect Market Segmentation Strategy?
The Long Tail theory is a transformative concept in today’s market environment, particularly in shaping effective market segmentation strategies. It revolves around targeting numerous niche markets with a broad range of products that have lower demand or sales volume, rather than concentrating solely on a few best-selling items. This approach is particularly significant in the digital age, where reduced costs of production and distribution enable businesses to economically offer a wider array of products.
The Influence on Consumer Behaviour
From a consumer behaviour perspective, the Long Tail theory highlights that customers are no longer limited to one-size-fits-all solutions. Instead, they actively seek products that better align with their individual needs and interests. The internet plays a pivotal role in this shift, providing consumers with the platform to explore and discover niche products that may be unavailable in traditional retail environments. This change in behaviour directly impacts customer market segmentation, requiring businesses to refine their strategies to cater to more specific and diverse customer needs.
Economic Implications
The Long Tail has significant economic implications for businesses. By embracing this model, companies can access new markets and boost overall sales. For instance, online giants like Amazon have excelled by offering millions of products, many of which fall under the Long Tail category—items that would be impractical to stock in physical stores. This vast product range not only attracts a broader audience but also enhances the effectiveness of customer market segmentation by allowing businesses to target a multitude of niche segments.
Production and Inventory Efficiency
The Long Tail model also influences production and inventory strategies. Instead of producing large quantities of a limited selection of products, companies can opt to manufacture smaller quantities of a broader variety of items. This approach fosters more efficient resource utilisation and can lead to a reduction in waste. For businesses employing market segmentation, this allows for a more tailored approach to inventory management, ensuring that products align more closely with the specific demands of segmented customer groups.
Marketing and Advertising Strategies
Marketing Long Tail products necessitates a different approach compared to traditional methods. Mass marketing techniques often fall short when addressing niche markets. Instead, businesses need to employ targeted marketing strategies that resonate with specific audiences. Utilising tools like social media and search engine optimisation becomes crucial in effectively reaching these segments. This precision in marketing not only aligns with the Long Tail theory but also enhances customer market segmentation by allowing businesses to connect more intimately with each segment.
Enhancing Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty
Offering a diverse range of products through a Long Tail strategy can significantly boost customer satisfaction. Consumers are more likely to find products that precisely meet their needs, leading to higher satisfaction levels. This satisfaction fosters greater customer loyalty and encourages repeat business, making the Long Tail approach an effective method within a broader market segmentation strategy.
Challenges and Risks
However, adopting a Long Tail strategy is not without its challenges. Managing a vast and diverse inventory can be complex and costly. There is also the risk that some niche products may not generate enough sales to justify their presence in the inventory. For businesses, this means that while the Long Tail approach can enhance market segmentation efforts, it requires careful management and strategic foresight to mitigate potential risks.
In-Depth Techniques for Targeting the Long Tail in Marketing
Successfully targeting the long tail in marketing requires a strategic approach that leverages both digital tools and customer insights. Below are key techniques to help businesses effectively engage with niche markets, aligning with a well-constructed market segmentation strategy.
1. Leverage Search Engine Optimisation (SEO)
Optimising your website’s content with long-tail keywords is crucial for reaching niche audiences. These more specific search terms help attract customers looking for particular products. Instead of broad keywords like “shoes,” focus on detailed phrases such as “handmade women’s leather boots” to capture more targeted traffic. By refining your SEO efforts around long-tail keywords, you enhance your market segmentation approach, ensuring that your content reaches the right customer segments.
2. Offer Personalised Products or Services
Customisation is a powerful tool for tapping into the long tail. By offering products or services tailored to individual preferences, businesses can cater to the unique needs of smaller, more specific customer segments. For example, Nike’s “Design Your Own” feature allows customers to create bespoke sneakers, appealing to those looking for something distinctly personal. This aligns perfectly with customer market segmentation by offering a tailored solution to niche audiences.
3. Implement a Recommendation System
Recommendation algorithms, similar to those used by platforms like Netflix, can be instrumental in connecting customers with relevant products. By analysing past purchases and customer preferences, businesses can suggest items that are more likely to appeal to individual buyers. This not only enhances customer satisfaction but also strengthens the effectiveness of your customer market segmentation by ensuring that each segment is presented with products that align with their interests.
4. Engage in Community Building
Fostering a sense of community around niche markets is another effective strategy for reaching the long tail. Online forums or social media groups dedicated to specific interests allow customers to engage with like-minded individuals. For instance, LEGO has successfully built a community of adult fans who share their custom designs and building techniques. By encouraging these interactions, businesses can tap into niche segments, reinforcing their market segmentation efforts and increasing brand loyalty.
Our Tactical Recommendations
To effectively reach your target segments, we recommend employing customer journey mapping, which helps you identify key touchpoints for engagement. Integrating feedback loops into your segmentation process ensures that you are consistently aligned with customer needs. Finally, leveraging behavioural insights can reveal opportunities that traditional demographics may miss, providing a richer understanding of your audience.Get In Touch
How Can a Business Use Market Analysis to Identify Opportunities?
A comprehensive market analysis is essential for identifying growth opportunities and refining your business strategy. Here are eight key types of analysis that businesses can leverage to uncover insights and strengthen their market segmentation strategy.
1. Consumer Segmentation and Behaviour Analysis
Understanding your audience by dividing them into distinct groups based on their characteristics helps you target the right people effectively. Customer market segmentation can be broken down by demographic factors (age, gender, income, education), geographic location (city, country, region), or behavioural traits (attitudes, lifestyles, etc.).
Demographic and geographic data allow you to estimate the potential size of your market. For instance, a baby food brand needs to understand the population of infants in countries where it operates, while an appliance manufacturer might analyse the number of households in a target region before expanding distribution.
Equally, behavioural factors are key, as they provide insight into customers’ motivations, such as price sensitivity or product positioning. Lifestyles and values can heavily influence purchasing decisions, so incorporating behavioural segmentation into your strategy ensures more targeted marketing.
To keep up with consumer trends, it’s important to monitor both short- and long-term shifts, like megatrends. For example, in response to inflation, some consumers have cut back on purchases, while others seek affordable indulgences. Premium snack brands like Mondelez with Toblerone Truffles and Mars with Trü Frü have capitalised on this trend by offering high-end treats at accessible prices.
Businesses that apply customer market segmentation to tailor their messaging and product offerings can significantly improve their marketing effectiveness.
Source: Mailchimp
2. Purchase Situation Analysis
The buyer’s journey is complex, influenced by a variety of factors that affect when, where, and how consumers make purchases. Understanding these patterns allows you to influence customer decisions at critical touchpoints. Consider the following:
- When do customers typically need or want your product or service?
- Where do they prefer to make purchases?
- How do they complete transactions?
By analysing these elements, businesses can adjust their distribution channels and payment methods to suit their customers’ preferences, helping to optimise sales.
For example, the retail sector has undergone significant change in recent years. The rise of convenience and discounter retailers has altered shopping habits, while livestreaming e-commerce has gained traction, particularly in China, where it is expected to surpass $450 billion in sales by 2024. Understanding these patterns can help you align your distribution strategy with evolving customer expectations.
3. Direct Competitor Analysis
Direct competitors offer similar products or services to your business. By conducting an in-depth analysis of these competitors, you can gain valuable insights into how they’re positioning themselves and identify opportunities for differentiation.
Key questions include:
- Which brands are experiencing growth, and why?
- What is their unique value proposition?
- How are they marketing their products?
- What competitive advantage does your business have?
For instance, before IKEA entered the Chilean market in 2022, it conducted extensive competitor research, assessing local players like Sodimac to determine how best to position its brand. Understanding your competitors’ strategies is key to spotting growth opportunities and refining your own approach.
4. Indirect Competitor Analysis
Indirect competitors target the same audience but sell different products that meet similar needs. Analysing these businesses can help you uncover market opportunities and refine your product offerings.
Take the travel industry as an example. Airlines might seek to capture market share from long-distance buses or trains. Questions to explore include:
- How many people are travelling long-distance by bus or train?
- What are the most popular routes?
- How much do travellers typically pay?
Similarly, companies in the food sector could analyse adjacent categories—such as snack bars versus yoghurt—to understand trends and identify innovation opportunities.
In the edible oils market, for example, strong price growth in sunflower oil has allowed producers of other oils to reevaluate their pricing strategies and boost profit margins. Exploring adjacent product categories provides additional insights into potential market opportunities.







