Imagine having the ability to tailor your campaigns so precisely that they resonate with your most valuable customers. But how do you determine these segments, and how can you effectively target them? This guide will take you through the essential steps, from understanding different types of segmentation to implementing strategies that drive real results.
Drawing from the latest tools and techniques, you’ll gain the insights needed to elevate your marketing efforts and see tangible improvements in your ROI.
- Understanding market segmentation is crucial for tailoring your marketing efforts to specific customer needs, leading to more effective campaigns.
- Different types of market segmentation, such as demographic, psychographic, and behavioural, allow for a more nuanced understanding of your audience.
- Strategic segmentation can significantly improve business performance by aligning marketing strategies with customer preferences.
- Conducting thorough market research and data analysis is essential to identify and target the most profitable customer segments.
- Practical examples and case studies demonstrate how successful companies have leveraged segmentation to enhance their marketing efforts.
- Overcoming challenges such as data quality and over-segmentation is vital for the effective implementation of segmentation strategies.
The 4 Types of Market Segmentation
A robust market segmentation strategy is crucial for businesses aiming to effectively target customer segments and optimise their marketing efforts. Market segmentation involves dividing a broad, homogenous market of potential customers into distinct, identifiable segments. Each segment consists of customers who share similar characteristics and exhibit comparable product needs, making them more likely to respond similarly to specific marketing strategies.
Given that most companies lack the resources to target a mass market, it becomes essential to focus on specific target customer segments. By employing a market segmentation strategy, businesses can identify and target market segmentation groups that are most likely to require their products or services.
What Matters Most?
Segmenting based on customer intent and behaviour patterns typically drives the highest return. Clients often discover that aligning their segmentation to firmographic data alone misses critical nuances. Instead, dynamically evolving segments using predictive analytics can yield much stronger results. Additionally, focusing on a customer’s emotional drivers—what motivates their decision-making—often reveals hidden opportunities within segments.Get In Touch
Demographic Segmentation
Demographic segmentation is the most widely used type of market segmentation. It involves dividing a target audience based on qualities such as age, gender, occupation, education, income, and nationality. This method is popular because demographic information is relatively easy and cost-effective to obtain. For example, body wash products are often segmented demographically, with variations marketed specifically for men and women.
Combining demographic segmentation with other types of segmentation can further refine your target market segmentation. This mixed approach allows for more precise targeting and messaging, enhancing the overall effectiveness of your marketing strategies.
Behavioural Segmentation
Behavioural segmentation categorises customers based on their behaviours and interactions with your product or service. By understanding these behaviours, businesses can tailor their messaging to better align with customer actions. Key behaviours include:
- Actions taken on a website
- Online shopping habits
- Brand loyalty
- Product usage rate
- Consumer needs satisfaction
This segmentation strategy enables marketers to create more effective segmentation strategies, as it directly relates to how consumers engage with their products.
Geographic Segmentation
Geographic segmentation divides a market based on location, such as town, county, zip code, or country. Despite its simplicity, this method is highly effective. Understanding where customers are located allows businesses to cater to their specific needs with location-specific ads and offers.
Marketers can also segment based on climate or population density, enabling even more targeted and relevant messaging. Additionally, considering language variations in different regions can enhance the effectiveness of geographic segmentation.
Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation delves deeper than demographics by focusing on mental and emotional attributes. This method divides customers based on personality traits, values, interests, attitudes, and lifestyles. While demographic data is easier to observe, psychographic information provides valuable insights into customer motives, preferences, and needs.
Integrating psychographic segmentation with demographic data can enhance the relatability and effectiveness of your marketing messages. If your demographic-focused messaging isn’t resonating, incorporating psychographic insights can provide a clearer understanding of why customers purchase or avoid certain products or services.
Top Benefits of Market Segmentation
Implementing a robust market segmentation strategy brings numerous advantages, allowing businesses to effectively target customer segments and optimise their marketing efforts. Here are the top benefits:
- Enhanced Customer Service: By accurately identifying the needs of your target customer segments, segmentation enables businesses to tailor their marketing efforts. This targeted approach enhances customer satisfaction and retention by providing compelling reasons to purchase and delivering a superior service to your audience.
- Improved Resource Efficiency: Customising marketing efforts towards specific target customer segments results in more efficient use of resources. This approach ensures that budgets are allocated to the most relevant segments, particularly when resources are limited. Consequently, businesses achieve a better return on investment compared to spreading efforts thinly across a broad audience.
- Stronger Marketing Messages: With market segmentation, you no longer need to rely on generic and vague messaging. Instead, you can craft communications that speak directly to the characteristics, wants, and needs of specific groups. This precision makes your marketing messages more relatable and impactful.
- Targeted Digital Advertising: A well-defined market segmentation strategy helps you understand your audience’s characteristics, enabling you to direct your marketing efforts to specific ages, locations, buying habits, and interests. This targeted approach improves the effectiveness of your digital advertising campaigns.
- Development of Effective Marketing Strategies: Knowing your target audience provides a head start in determining which methods, tactics, and solutions will be most effective. This insight allows you to develop more effective segmentation strategies tailored to the preferences of your audience.
- Better Response Rates and Lower Acquisition Costs: Effective segmentation leads to more precise marketing communications, both in ad messaging and advanced targeting on digital platforms like Facebook and Google. This precision results in better response rates and lower acquisition costs, making your marketing efforts more efficient and cost-effective.
Source: NotifyVisitors
What steps should I follow to develop an effective market segmentation strategy?
Step 1: Set Clear Objectives
The initial step in crafting a market segmentation strategy is to set clear objectives. Define the goals and expectations of your market segmentation efforts to ensure a focused approach.
Step 2: Collect Data Through Market Research
Effective segmentation begins with comprehensive market research, which extends beyond understanding your customers to gaining a macro-level view of the entire marketplace. Utilise online focus groups, in-person interviews, surveys, or polls to gather data. Tools like Alexa and Quantcast can provide an overview of your customers, while resources such as the US Census Bureau can offer valuable demographic information, including income, education, gender, and age.
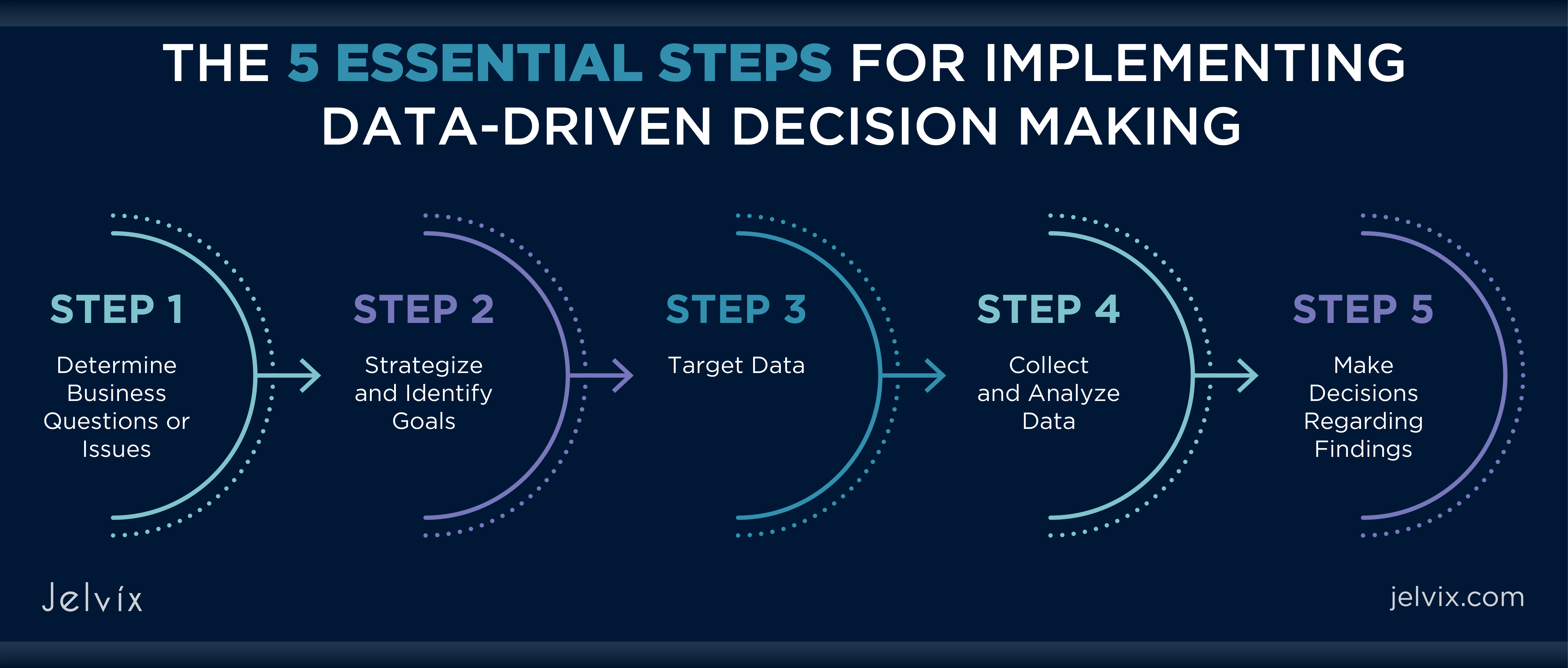
Step 3: Create Buyer Personas
Developing buyer personas involves creating semi-fictional representations of your target customer segments. Use a combination of third-party research and your own insights to craft these personas. Collect feedback from your sales team and send out customer surveys to gather pertinent information. Once collected, organise this data to form distinct buyer personas that accurately reflect your various customer segments.
Step 4: Build Marketing Strategies
With your buyer personas in place, identify the market segments most relevant to your brand. Many companies use a mix of segmentation strategies to formulate their marketing approach. Choose strategies that align naturally with your identified target market segmentation. Potential strategies include pricing, expansion opportunities, and niche markets.
Step 5: Test a Marketing Strategy That Works
After identifying your segments, test your findings and review the customer segments, making necessary adjustments. Develop segmented marketing campaigns that speak directly to your customer personas, focusing on unique values or beliefs that resonate best with them.
Our Tactical Recommendations
Many clients find that creating self-segmentation options—where prospects select their own journey—leads to better-qualified leads. Another key actionable step is using customer feedback loops, such as reviews and conversational marketing, to adjust and refine your segments regularly. Clients often discover the power of hyper-targeted content; when mapped to specific behavioural traits within each segment, it drives higher engagement and conversions.Get In Touch
What are the types of market segmentation strategies I can use?
Concentration Strategy
A concentration strategy involves focusing efforts on a single market segment. This approach is particularly advantageous for small, growing businesses with a specific market use case. Concentrating on one segment allows for the investment of more time, energy, and resources, minimising advertising spend and reducing the risk of spreading efforts too thin.
- Pros: High conversion rates, repeatable marketing practices, reduced marketing spend.
- Cons: Limited growth potential confined to the segment size, high risk if the segment is not properly vetted.
Multi-Segment Strategy
Multi-segment marketing, also known as differentiated marketing, involves designing strategies to market a product to more than one segment. While seemingly safer than a concentration strategy, it demands a larger marketing budget as it necessitates distinct campaigns for each market segment.
- Pros: Appeals to a broader audience, diverse marketing approaches, high growth potential.
- Cons: Lower conversion rates per segment, greater overall marketing spend.
By meticulously applying these steps and strategies, businesses can achieve more effective segmentation, ensuring that marketing efforts are precisely targeted and resource-efficient. This approach not only optimises marketing performance but also enhances customer satisfaction and drives growth.
Utilising Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning (STP) for Effective Marketing Strategies
The STP framework, which stands for Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning, is a strategic approach that allows businesses to analyse their products or services and effectively communicate their value to distinct customer segments. This model guides you through segmenting your audience, focusing on specific target customer segments with customised marketing campaigns, and positioning your brand to meet their unique preferences and expectations.
Step 1: Segmentation
The first phase of the STP process is segmentation. This involves dividing your overall market into distinct customer segments based on selected criteria. The objective is to identify groups with similar characteristics, allowing for more precise targeting. The main types of segmentation include:
- Geographic Segmentation: Segmenting the audience by location—such as country, region, or city.
- Demographic Segmentation: Classifying based on factors like age, gender, education, and occupation.
- Behavioural Segmentation: Grouping customers according to their behaviour—such as purchasing habits, frequency of purchases, and online interactions.
- Psychographic Segmentation: Dividing the audience by lifestyle, values, interests, and opinions.
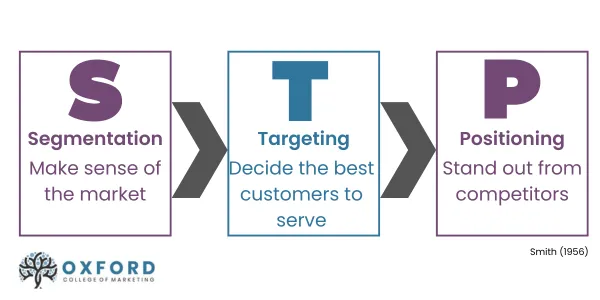
Step 2: Targeting
Once the segmentation is complete, the next step is targeting. Here, the goal is to identify which of the customer segments are most likely to deliver the desired outcomes—whether that’s sales, leads, or other key conversions.
The ideal target segment is one that is experiencing growth, offers high profitability, and has a manageable cost of acquisition. When selecting your target segments, consider:
- Size: Assess the potential growth and sustainability of the segment.
- Profitability: Identify which segments are willing to invest the most in your product or service, and calculate the lifetime value of customers within those segments.
- Reachability: Evaluate how accessible the segment is and consider the customer acquisition cost (CAC). Higher CACs can reduce profitability, so balance is key.
Choosing the right target segments requires careful consideration of multiple factors to ensure alignment with your business objectives and market opportunities.
Step 3: Positioning
The final step in the STP model is positioning. Positioning involves defining how your product or service should be perceived by the selected target customer segments compared to competitors. Given the competitive landscape, finding and articulating what makes your offering unique is critical.
The insights gained from your segmentation and targeting efforts should clarify your market niche. Effective positioning can be achieved through three primary approaches:
- Symbolic Positioning: Enhancing the customer’s self-image, sense of belonging, or ego—luxury brands often use this strategy to elevate their products beyond mere functionality.
- Functional Positioning: Solving specific customer problems and providing clear, tangible benefits.
- Experiential Positioning: Building an emotional connection between the customer and your brand, product, or service.
The most effective positioning strategies often incorporate all three elements. A practical tool to visualise your positioning within the market is a perceptual map, which can help you identify where you stand in relation to competitors and what factors are most important to your customers.
Examples of STP Marketing
There are several approaches to STP marketing, including:
- Vertical Market: Targeting multiple segments within a single vertical can help you reach smaller segments in your industry. Position a specific product or service to appeal to different segments within one market.
- Horizontal Market: Instead of focusing on a single vertical, horizontal marketing targets segments across various industries that share characteristics. This approach is often used by small businesses.
- Product Line Extensions: Expanding your company’s reach by adding new products tailored to different market segments’ unique needs.
- Positioning: This approach focuses on positioning a single product or service by highlighting customers’ problems and demonstrating how your solution addresses those pain points.
The best option for your business depends on your goals, marketing capabilities, and competitive landscape. By meticulously applying the STP model, you can develop a marketing strategy that effectively targets customer segments, optimises resource allocation, and enhances overall marketing performance.
Market Segmentation Pitfalls
When crafting a market segmentation strategy, it is crucial to be aware of common pitfalls that can undermine your efforts. Here are some key challenges to watch out for:
- Insufficient Data: Relying on a single data point does not provide a comprehensive view of your market. The more data you have, the better your analysis will be, as larger data sets help mitigate the impact of outliers. To achieve statistically significant findings, ensure you collect a substantial amount of data.
- Unclean Data: An efficient and automated data collection process is essential, but it’s not enough to just gather data. You must standardise it into a usable format immediately upon collection. This involves aligning data from various sources into consistent formats and removing duplicates. Without clean data, drawing accurate conclusions becomes impossible.
- Non-Specific Market Segments: Creating overly broad market segments can lead to ineffective marketing efforts. While it might seem beneficial to keep segments broad to avoid frequent updates, this approach often backfires. Broad segments lack the specificity needed to be relevant and effective. Ensure your segments are narrow and detailed enough to provide meaningful insights and actions.
- Over-Reliance on Past Behaviours: While behavioural segmentation is a powerful tool, relying solely on past behaviours to predict future events can be limiting. Geographic and demographic segmentation also play vital roles and should not be overlooked. A balanced approach that incorporates various segmentation methods will provide a more comprehensive understanding of your target customer segments.







