Whether you’re offering software, curated products, or exclusive services, a well-structured subscription model can secure a stable, recurring revenue stream. However, managing and scaling a subscription model comes with unique challenges, from keeping customers engaged to efficiently handling massive amounts of data.
In this guide, you’ll discover how to choose the right subscription model for your business, retain customers through added value, and streamline operations using automation tools. You’ll also learn how leading companies like Amazon and Netflix have mastered subscription-based growth.
- Subscription models ensure stable, recurring revenue: By offering products or services through a subscription model, businesses can rely on consistent revenue streams rather than one-time transactions.
- Customer retention is key: In a subscription-based business, long-term success depends on retaining customers by consistently adding value at each renewal cycle.
- Automation is crucial for data management: Managing subscriptions involves handling vast amounts of customer data, from payment details to service preferences. Automation tools can streamline these processes, ensuring efficiency and scalability.
- Adopt a customer-centric approach: Building lasting relationships with customers through personalised interactions and continuous engagement helps reduce churn and improve loyalty.
- Selecting the right subscription model: Whether it’s SaaS, box subscriptions, or membership models, the success of your subscription strategy depends on choosing a model that aligns with your product offerings and customer needs.
- SaaS models require consistent value delivery: For SaaS companies, ensuring that customers always have access to the latest features and updates is key to maintaining satisfaction and retention.
- Scalability is essential: As your customer base grows, your subscription model must be flexible enough to accommodate both small and large businesses, ensuring continued value.
- Examples of successful subscription businesses: Companies like Amazon Prime and Netflix have mastered subscription models by providing constant value and evolving their offerings to meet changing customer expectations.
How do different sectors implement a subscription business model?
A Closer Look at the Subscription Business Model
The subscription business model is a time-tested strategy that has been effectively utilised across various industries for decades. It operates on a simple yet powerful principle: customers pay a predetermined fee at regular intervals, such as monthly or annually, in exchange for access to a product or service. This approach not only ensures that customers receive what they need on a consistent basis, without the need for repeated transactions, but it also provides businesses with the stability of predictable, recurring revenue—a key component of a robust subscription business model.
What Matters Most?
We typically see that what drives the most sustainable subscription businesses is the ability to deliver ongoing value that extends far beyond the initial sale. Clients often discover that continuous engagement, rather than simply onboarding, keeps customers loyal for the long term. Equally, a flexible pricing model that grows with the customer is essential for retaining their business as their needs evolve. Typically, we find that a well-structured onboarding and engagement plan, one that ensures early customer success, is crucial for reducing churn and establishing a foundation for a lasting relationship throughout the subscription journey.Get In Touch
While not every industry naturally aligns with the subscription business model, there are several sectors where this approach has proven to be particularly effective. Here, we explore four industries that have successfully adopted this model, showcasing its versatility and broad appeal.
1. Online Learning
Traditional education has long relied on the in-person classroom model, with a teacher guiding around 25 students through a standardised curriculum. However, the rise of online learning platforms, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, has revolutionised access to educational resources. These platforms provide flexible learning opportunities to people of all ages, enabling them to engage with educational content from anywhere in the world.
Several online learning platforms have embraced the SaaS subscription business model to deliver educational content:
- Educator.com offers a comprehensive range of middle school, high school, and college-level courses, taught by experienced educators, for a modest monthly fee. This platform is ideal for students seeking additional support or for lifelong learners.
- Treehouse provides unlimited access to coding courses for just $25 per month, with a free trial available, making it an accessible resource for budding developers.
- Udemy boasts a vast library of over 200,000 courses covering business, design, marketing, and more, with flexible pricing options to meet the diverse needs of learners.
These platforms demonstrate the advantages of SaaS pricing models, allowing users to explore new skills and subjects at their own pace, akin to a buffet-style learning experience, where the only limit is their curiosity.
Tip: Consider offering your employees access to an online learning subscription as part of their professional development. This approach not only enhances their skills but also contributes to a more knowledgeable and capable workforce.
2. Streaming Entertainment
The streaming industry is perhaps one of the earliest adopters of the subscription business model, particularly in music and video entertainment. Apple Music, with its 88 million subscribers in 2021, and Spotify, with over 188 million subscribers, exemplify how this model has reshaped the way we consume music.
Similarly, subscription-based video streaming services such as Netflix, YouTube TV, HBO Max, Hulu, and Apple TV have transformed the entertainment landscape. These platforms leverage the increased availability of internet-enabled devices to offer unlimited streaming options, eliminating the need to purchase individual songs or films. This shift underscores the potential of SaaS pricing strategies in driving digital disruption.
3. Beauty and Health Products
The beauty and health sectors have also found immense value in the SaaS subscription business model. Birchbox, a pioneer in this space, launched in 2010, offering curated samples delivered directly to consumers’ doors for just $10 per box. This model has since expanded to include a wide array of personalised beauty and skincare products, available through various subscription tiers.
Today, the market is brimming with subscription-based beauty and health services, including:
- Billie, offering razor sets and skincare products.
- Flamingo Estate, specialising in at-home spa products.
- The Detox Market, providing ethically sourced beauty products.
- Skylar Scent Club, delivering monthly fragrance selections.
- Dermstore, offering high-end skincare solutions.
- Petit Vour, focusing on vegan beauty boxes.
These companies exemplify the adaptability of subscription business models within the beauty and health industry, enabling consumers to easily maintain their preferred routines without the hassle of reordering.
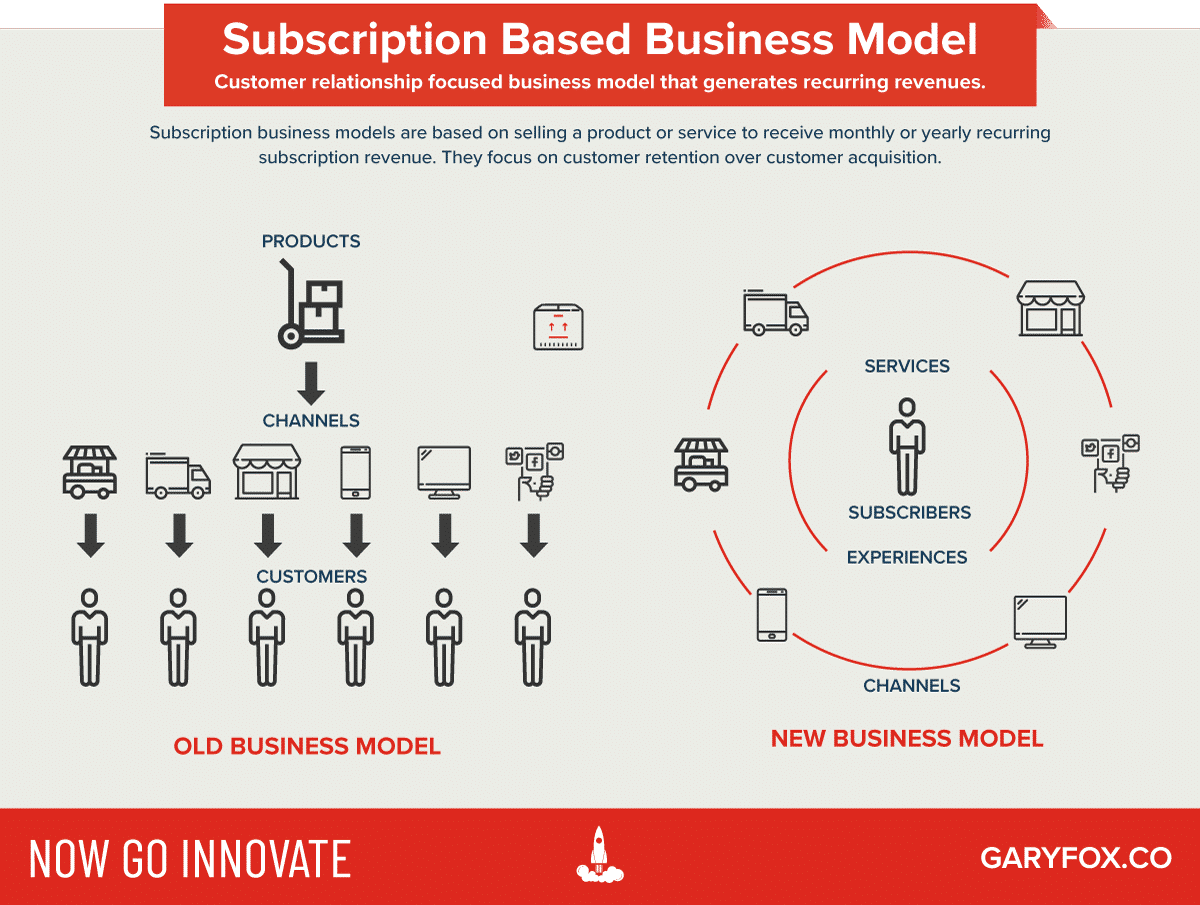
How do customers typically subscribe to a subscription business model?
The subscription business model has seamlessly integrated into the daily lives of consumers, with many spending significant sums on these services monthly. On average, Americans spend around US$219 per month on subscriptions, highlighting the ubiquity and appeal of this model. Below is a detailed exploration of the different types of subscription business models that have gained traction across various industries.
Membership Subscriptions
Membership subscriptions offer exclusive access to specific services or products in exchange for a regular fee. This model is typified by gym memberships or online clubs, where the value proposition lies in being part of a select group that enjoys unique perks—whether that’s special content, services, or other benefits that are not available to non-members.
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) Subscriptions
The SaaS subscription business model has revolutionised how we access software. Rather than making a one-time purchase, users subscribe to access the software, ensuring they always have the most up-to-date version. The provider handles all updates and maintenance, offering a hassle-free experience that is particularly appealing in today’s fast-paced digital environment. This model not only simplifies access but also aligns with evolving SaaS pricing strategies that optimise revenue through recurring payments.
Box Subscriptions
Box subscriptions deliver a curated selection of items—ranging from food and beauty products to books—on a regular schedule. The allure of this model lies in the element of surprise and the convenience of having these curated items delivered directly to the customer’s door. This model thrives on the personalisation and discovery aspects that keep consumers engaged month after month.
Source: McKinsey
Content Subscriptions
In the realm of digital media, content subscriptions have become the norm. Users pay a recurring fee to access a vast library of content, such as news articles, videos, or music. Streaming platforms like Netflix and Spotify exemplify this model, where continuous access to a rich variety of content is exchanged for a subscription fee. This model capitalises on the increasing demand for digital content consumption and is a staple in SaaS pricing models.
Usage-Based Subscriptions
Usage-based subscriptions are dynamic and flexible, charging customers based on the amount of service used. A traditional example is the electricity bill, which fluctuates depending on consumption. In the digital age, this model has evolved, with cloud services charging based on data storage or bandwidth usage. This model is increasingly popular due to its scalability and alignment with customer usage patterns.
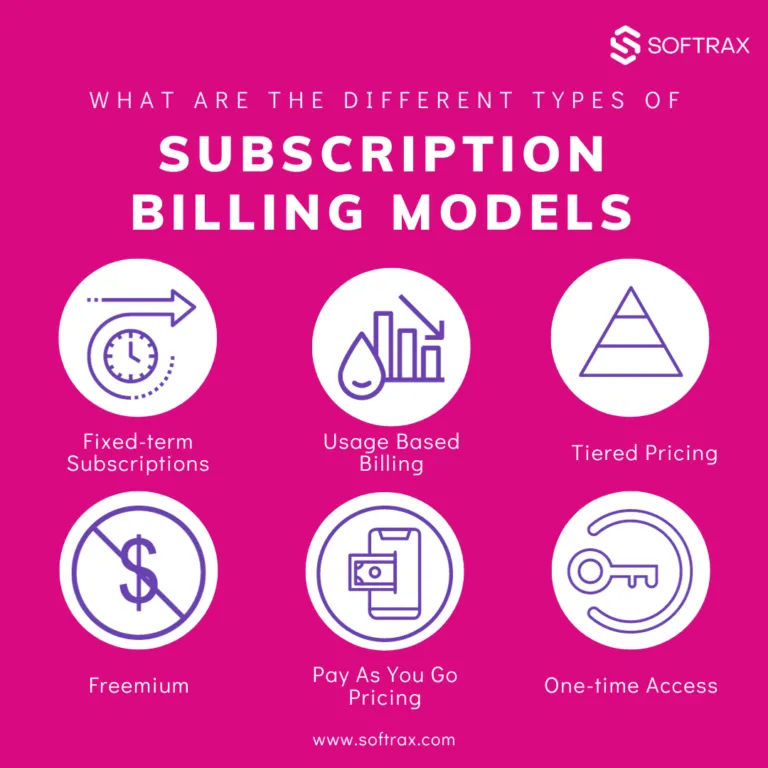
Freemium Subscriptions
The freemium model offers a basic version of a service at no cost, while advanced features are locked behind a paid subscription. This approach is common in apps and online services, where the free version often includes ads or limited functionality. As users grow more reliant on the service, they are encouraged to upgrade to a premium version, aligning with sophisticated SaaS pricing strategies designed to convert free users into paying customers.
Community Subscriptions
Community subscriptions focus on building a network or community around a particular service or product. Often combined with a membership model, the real value here is in the connections and network benefits provided to subscribers. This model fosters a sense of belonging and shared purpose, making it particularly effective in niches where community engagement is key.
By leveraging these varied subscription business models, companies can effectively engage their target audience, ensuring sustained growth and customer retention. Each model offers unique benefits, tailored to different consumer needs and preferences, making them powerful tools in the modern business landscape.
7 Critical Considerations When Selecting a Subscription Pricing Model
1. Determining Your Value Metric(s)
A value metric, sometimes referred to as a pricing axis or dimension, is the fundamental basis upon which your pricing is structured—essentially, what and how you are charging. We’ve touched upon some common value metrics, such as users and features, but businesses may also consider metrics like:
- Length of subscription
- Available bandwidth (measured in terabytes)
- Number of tickets or queries received
- Volume of documents created
- Support sessions provided
- Data capacity required
- Compute power utilised
- Percentage of revenue generated by the service
- Amount of storage used
- API requests made
- Number of campaigns run
To ensure your SaaS pricing strategy is optimised, compile a comprehensive list of potential pricing axes and evaluate each one using these key questions:
- Is it predictable?
A value metric should be reasonably predictable for both your business and your customers. Both parties need to anticipate costs and revenues accurately. For example, a pricing model based on the number of landing page visitors might introduce unpredictability, whereas charging upfront for a specific number of contacts per tier offers clarity and stability. - Is it acceptable to customers?
The chosen value metric must be easily understood by sales teams and customers alike. If the pricing structure is confusing or too complex, potential clients may hesitate to commit. For example, a small business might be deterred by a pricing structure that seems geared towards larger enterprises. - Is it trackable?
The ability to track the value metric is crucial. For instance, if you’re charging based on a customer’s revenue, they would need to provide access to sensitive financial information—an often challenging requirement. - Is it scalable?
The scalability of the value metric is vital for long-term growth. The SaaS subscription business model should be able to accommodate both small and large businesses, ensuring that the model grows alongside the customer’s needs. - Is it aligned with value?
Your pricing should reflect what customers truly value in your product. Assess which metrics most closely align with the benefits your service provides, ensuring that the pricing correlates with the perceived and actual value delivered.
2. Evaluating Time and Resource Requirements
When selecting a subscription business model, it’s important to consider the time and resources needed to manage it effectively. Complex pricing models, such as those based on usage, require robust tracking and billing systems, which can increase operational complexity. Conversely, a flat-rate model might be more appropriate for companies whose subscription services represent a smaller portion of their overall business, reducing administrative burden.
3. Aligning with Your Offering
The nature of your offering will significantly influence your choice of pricing model. For businesses with multiple upsell or cross-sell opportunities, a flat-rate model may not capture the full value of these additional features. Conversely, products with usage that is difficult to quantify might not be well-suited to usage-based pricing, making alternative models more appropriate.
4. Understanding Your Customer Base
A deep understanding of your customer base is essential when designing a SaaS pricing strategy. Consider customer preferences, usage patterns, and willingness to pay. Surveys and interviews can be invaluable tools for gathering insights, helping you tailor your pricing model to meet customer expectations. For example, understanding whether your customers prefer simplicity or customisation in their payment plans can guide your choice between flat-rate and tiered models.
Source: Zion Market Research
5. Analysing Competitor Strategies
Competitive analysis is a critical component of developing a successful SaaS subscription business model. Assess how your competitors structure their pricing and identify any gaps that your model could fill. For example, if competitors are primarily targeting large enterprises, a tiered pricing strategy with lower entry points might attract smaller businesses that are currently underserved.
6. Assessing Your Financials
Your chosen pricing model must cover both fixed and variable costs while ensuring profitability. For instance, a flat-rate model might struggle to remain profitable if some customers consume significantly more resources than others. In such cases, a usage-based model could help balance the load, generating healthier margins and ensuring sustainable growth.
How Do Companies Implement a Subscription Business Model?
Successfully adopting a subscription business model requires the integration of tools and processes that facilitate a seamless buying journey for customers, even as they interact across multiple channels or modify their subscriptions over time. It is essential to track new metrics to ensure your strategy is on the right track.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you implement a subscription business model effectively:
1. Empower Customers to Purchase and Pay Across Any Channel
In the realm of subscription selling, continuous interaction with your customers is crucial, and it’s increasingly evident that customers prefer to engage on their own terms. Whether they’re in the comfort of their home or on the go, they expect the ability to renew, upgrade, and make payments with ease—without needing to pick up the phone.
A recent McKinsey report highlighted that “more than three-quarters of buyers and sellers now prefer digital self-serve and remote human engagement over face-to-face interactions.” To meet these evolving expectations, your business needs to provide the flexibility for customers to manage their subscriptions via their preferred channels, whether through a website, mobile app, or another digital platform.
2. Prioritise Delivering Customer Value
The essence of a successful SaaS subscription business model lies in consistently delivering value to your customers. The ongoing nature of subscriptions means you’re frequently asking customers to renew their commitment to your service. If they don’t perceive continuous value, they’ll simply churn, leading to stalled growth.
To ensure sustained customer satisfaction and retention, shift your focus from merely shipping products to delivering value-as-a-service. Consider how companies like Netflix have transformed from shipping DVDs to providing entertainment-as-a-service, or how Amazon excels at delivering exceptional buying experiences rather than just products. The key is to consistently add value at every stage of the customer journey.
This approach places a significant emphasis on your service and customer success teams, who must collaborate to ensure that customers are not only adopting your product but also finding continuous satisfaction with it.
3. Measure Recurring Revenue with New Metrics
In the world of subscriptions, the spotlight has shifted from customer acquisition to customer retention and value—metrics that directly drive recurring revenue. However, to effectively grow retention, you must have reliable methods to measure it.
Start by focusing on customer value metrics. For instance, you can gauge customer value by tracking how deeply customers are engaging with your subscription product or service. A key metric here is Average Revenue Per User (ARPU), which is calculated by dividing your total revenue by the number of active users. As your business evolves and you become more adept at targeting customers with the right offerings, ARPU should naturally increase, indicating that your SaaS pricing strategy is effectively enhancing customer value and retention.
Our Tactical Recommendations
In our experience, predictive analytics is a game-changer for identifying customers at risk of churn. Clients often use this approach to intervene early, resulting in improved retention rates. We also recommend regularly testing and optimising pricing models through A/B testing to stay competitive while maximising profitability. Finally, designing a frictionless experience—whether in onboarding, billing, or customer interactions—makes a significant impact on satisfaction and churn reduction. The smoother the customer journey, the more likely they are to stay engaged and continue renewing their subscription.Get In Touch
How to Add a Subscription Model to Your Business
1. Assess Whether a Subscription Model is Suitable
Before diving into a subscription business model, it’s crucial to evaluate whether this approach aligns with your product or service offering. Products that require regular replenishment or have an element of collectability are prime candidates. For instance, a business selling board games might thrive with a subscription model, offering customers a new challenge each month. Conversely, if you’re selling one-off items like dresses for sixth-form balls, a subscription service is less likely to be viable, as it doesn’t meet the recurring needs of your customer base.
2. Develop Your Membership Model
The next step is to determine how much to charge for your subscription. Your pricing should reflect the cost of goods sold, including shipping, marketing expenses, and other operational costs such as rent and payroll. Conduct thorough research into profit margins to ensure your pricing strategy is sustainable.
When establishing your SaaS pricing models, a one-size-fits-all approach might alienate certain segments of your customer base. To cater to a broader audience, consider implementing a tiered pricing model. This allows you to offer discounts for longer commitments or to specific groups, such as students. Over time, you should adjust your pricing based on customer feedback and market conditions, while striving to maintain consistency for existing subscribers.
Additionally, explore the freemium model as part of your SaaS pricing strategy. This approach offers basic access at no cost, enticing users to upgrade to a premium service once they’ve experienced the value of your offering. A notable example is LinkedIn, which provides basic features for free but charges for enhanced capabilities, such as premium resumes.
Setting the delivery cadence—whether weekly, monthly, or quarterly—is also essential. Tools like Square Payment Links can help you establish and manage your desired subscription intervals efficiently.
3. Define Clear Terms and Conditions
It’s imperative to establish clear terms and conditions that outline how your subscription works, including details on auto-renewals and cancellation policies. The UK Government has strict consumer protection laws governing these aspects, requiring that auto-renewals are transparent and cancellations are straightforward.
One effective method to ensure customer understanding is through a “clickwrap” agreement, where customers must actively agree to the terms during the subscription process by checking a box. This method helps protect your business and ensures customers are fully aware of their commitments.
4. Prepare and Manage Inventory
With the groundwork laid, the next step is to plan and prepare your inventory. If you are providing physical products, securing reliable suppliers is crucial to meet the demands of your subscribers. For those creating products in-house—like a coffee shop offering a monthly blend subscription—control over production will be key to maintaining consistency and quality.
5. Communicate Your Subscription’s Value
Marketing your subscription is about more than just selling a product—it’s about building a relationship between your brand and your customers. To do this effectively, you need to clearly communicate how your subscription will enhance their lives.
It’s important to maintain ongoing engagement with your customers. Simply securing a subscription isn’t enough to ensure long-term loyalty. Regular communication, personalised outreach, and VIP touches—like early access to new products—can help nurture these relationships. Over time, customers will come to expect increasingly tailored experiences, so be prepared to adapt your offerings to meet their evolving needs.
What are some challenges of running a subscription business model?
Redeploying Sales Staff
In traditional sales models, a transaction typically concludes once the sale is made, with limited ongoing interaction between sales staff and customers. However, in a subscription business model, the relationship is ongoing, necessitating a greater emphasis on customer engagement and retention.
This shift may require retraining sales teams to focus on building long-term relationships rather than simply closing deals. Teams should be structured to blend sales and customer service roles, allowing them to address customer concerns while also identifying opportunities for upselling or cross-selling. This approach ensures customers continue to see value in their subscription, enhancing loyalty and reducing churn.
Organising Data Efficiently
Managing a subscription model involves handling vast amounts of data, from customer information and payment details to subscription preferences and renewal dates. A robust business infrastructure is necessary to organise this data efficiently, ensuring it is accessible to both your team and your customers.
Automation tools, such as those offered by Chargebee, can simplify the process of data management, making it easier to handle the complexities of a SaaS subscription business model. These tools not only streamline operations but also scale with your business, allowing you to focus on growth without worrying about data handling capabilities.
Adding Value at Each Renewal Cycle
One of the greatest advantages of a subscription business model is the potential for consistent, recurring revenue. However, this benefit also comes with the challenge of continuously proving value to your customers. Each billing cycle is an opportunity for customers to reassess the value they receive, making it crucial for businesses to consistently add value.