Imagine a scenario where every interaction with your customers leads them naturally to their next purchase, increasing their value to your business each time. This is the essence of a well-crafted value ladder. But how do you construct this ladder to maximise customer value and scale your business effectively?
The secret lies in understanding the strategic placement of each rung on the ladder and how it aligns with your customers’ journey. In this guide, we’ll explore the step-by-step process of building a value ladder, revealing how it can transform one-time buyers into loyal, high-value customers. Ready to elevate your business to the next level?
- A well-designed value ladder is crucial for transforming one-time buyers into loyal, repeat customers.
- Each step of the value ladder should be strategically aligned with the customer journey to maximise engagement and sales.
- Overcoming common challenges in building a value ladder requires a deep understanding of customer needs and preferences.
- Continuous optimisation and technology integration are key to maintaining the effectiveness of your value ladder.
- Measuring success through KPIs like customer retention and average order value ensures that your value ladder delivers tangible business growth.
What are the initial offerings in a value ladder strategy?
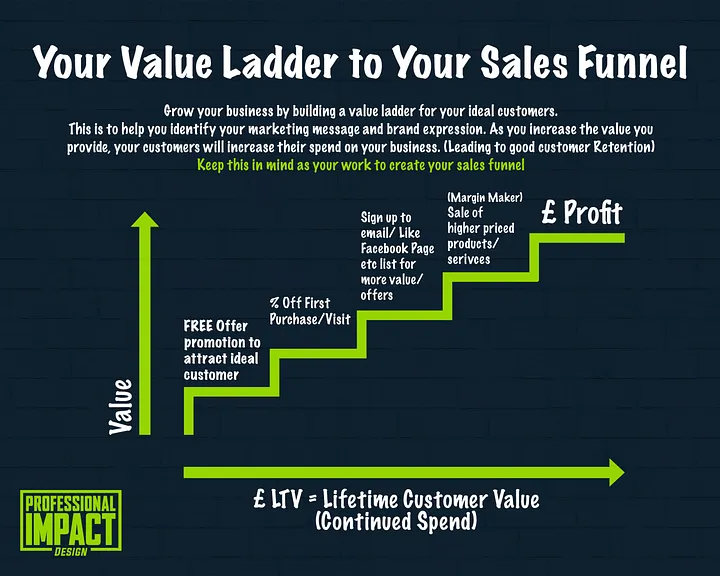
A value ladder represents a strategic approach in marketing where a brand systematically increases the value it offers to customers, encouraging them to spend more over time. This dynamic relationship often starts with a low-cost or free offering, gradually leading to higher-priced services or products as trust and engagement grow. The key to a successful value ladder is providing incremental value at each step, fostering a deeper customer relationship.
What Matters Most?
We’ve found that strategic alignment across teams is pivotal when building a successful value ladder. Clients often discover that integrating sales, marketing, and customer success around a shared vision is the key to accelerating customers’ movement up the ladder. Typically, personalising each step of the value ladder based on customer behaviour leads to smoother transitions. In our work, we’ve also seen that focusing on long-term relationships fosters deeper loyalty, helping companies guide their clients through higher-value offerings without losing sight of customer satisfaction.Get In Touch
For instance, consider a coach who begins by sharing free videos on platforms like YouTube or social media. Some viewers might then join a free community. Within this community, a subset might opt for group coaching sessions, and a few might progress to one-on-one coaching at a premium price. Each step on this value ladder not only increases the cost but also the value provided, making it a progressive journey for the customer.
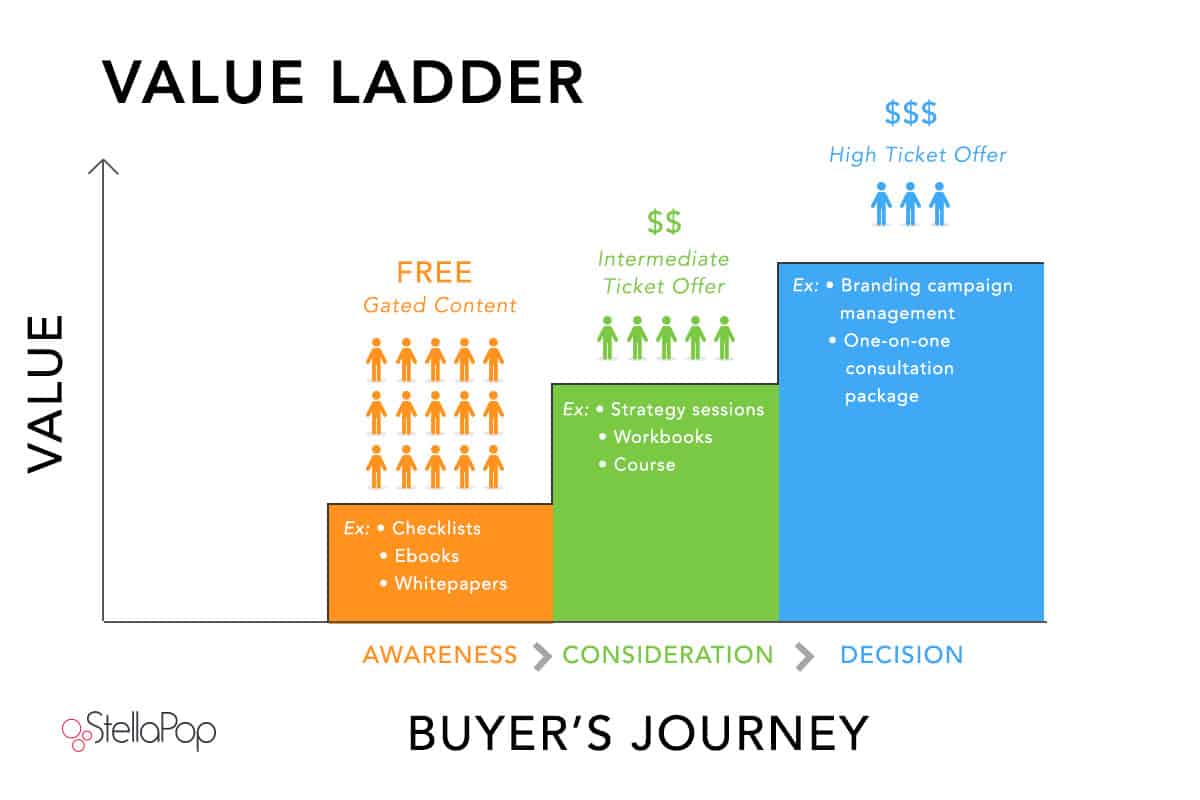
Imagine constructing a ladder tailored for your ideal customer. Each rung on this ladder represents a more valuable and pricier offer than the last, enabling customers to ascend gradually, experiencing increased value at every step.
For information products, your value ladder could include:
- Free Content (Twitter, Newsletter, blogs)
- Free guides and cheat sheets
- Low-priced eBooks and courses
- High-priced courses and community memberships
- Premium coaching and consulting services
For software products, the ladder might look like this:
- Free version (with limited features)
- Low-priced version (restricted usage and features)
- High-priced version (full feature set)
- Premium version (full features plus priority onboarding and support)
This model is advantageous as it allows you to develop more sophisticated offerings over time, mirroring the growth of your customers.
Importance of a Value Ladder Strategy
A well-crafted value ladder strategy offers numerous benefits. Primarily, it helps build trust and credibility with your customers. By delivering substantial value upfront, often at no cost, you demonstrate your expertise and willingness to assist, laying a strong foundation for future transactions. This initial positive interaction encourages customers to explore your higher-tiered, more expensive offerings.
Moreover, a value ladder nurtures long-term relationships. As customers progress through the ladder, experiencing increasing value, they are likely to become loyal advocates of your brand. This loyalty translates into repeat business, referrals, and positive word-of-mouth, all of which are critical for sustained business growth.
What are the differences between micro and macro value ladders?
Understanding the distinction between micro and macro value ladders is essential.
Micro Value Ladder A micro value ladder is akin to a sales funnel. In this scenario, you present the next step of the ladder within the same transaction. It often involves quick, incremental upgrades or add-ons. For example, when a customer purchases a product, they might immediately be offered an upgrade or additional features at a slightly higher price. This process is rapid and can increase the average transaction value efficiently.
Macro Value Ladder Conversely, a macro value ladder is more of a ‘customer journey.’ This approach recognises that some customers may take months or even years to progress to the next rung. It involves a long-term strategy where customers are gradually nurtured and guided through various stages of engagement and value recognition. This type of ladder is particularly effective for building deep, lasting customer relationships and significant brand loyalty.
Micro Value Ladder Example
Trey Lewellen, a renowned Internet marketing expert, successfully launched a funnel that generated over $20 million in just six weeks, a record yet to be surpassed. His strategy revolved around selling tactical flashlights through a well-crafted micro value ladder.
A customer initially purchased a tactical flashlight for approximately $18. Immediately following this purchase, they were offered rechargeable batteries and then the option to buy a 1-year or 3-year warranty. This simple yet effective value ladder ensured customers saw continuous value at each step, boosting overall sales.
Macro Value Ladder Example
Elon Musk understood the importance of delivering substantial value before customers were ready to purchase a Tesla. To achieve this, Tesla stores feature coffee bars, Wi-Fi access, and open service bays, creating a welcoming environment with no pressure to buy.
Visitors could simply drop in, enjoy a coffee, and observe the service bays. Inside the store, they could watch “Tesla Stories,” showcasing real owners’ experiences with electric cars. Potential customers could then design their own roadster and share it on social media. If interested, they could sign up for a free test drive. Finally, for those ready to purchase, Tesla offered a range of cars at various price points, building trust and perceived value progressively.
By meticulously implementing a value ladder strategy, you can guide your customers through a journey of increasing value, enhancing their experience, and driving long-term business growth. This approach not only boosts immediate sales through micro ladders but also fosters deep, loyal customer relationships through macro ladders, ensuring sustained success.
How can I effectively implement a value ladder strategy?
Implementing a value ladder strategy involves several key steps:
- Initial Offer (First Rung): Start with a low-cost or free offer to attract potential customers. This initial offer serves as an entry point, allowing them to experience your value with minimal risk.
- Middle Offers (Middle Rungs): As customers ascend the ladder, introduce more valuable and higher-priced offerings. This could involve upselling, cross-selling, or enhancing the initial offer with additional features or benefits.
- Premium Offer (Top Rung): The final stage is your highest-priced, most valuable offering, often accompanied by exclusive access or personalised support. By this point, customers should trust your brand and recognise the value of your premium products or services.
Practical Example of a Value Ladder Strategy
Consider a business offering marketing automation software:
- Free Version: Limited features to attract new users.
- Basic Version: Low-priced with additional features for moderate use.
- Pro Version: Full feature set for advanced users.
- Enterprise Version: Premium features with priority support and customisation.
By following this structured approach, you can effectively guide your customers through a journey of increasing value, enhancing their experience while driving business growth.
Stages of the Value Ladder Strategy
- Bait — Begin by attracting prospects into your ecosystem with a free, high-value offer. This initial step is crucial for establishing immediate trust and rapport with new prospects. Examples include free eBooks, insightful webinars, or exclusive content downloads.
- Front End — At this stage, you encourage the prospect to transition into a customer with a compelling and heavily discounted offer. Think of deals like a free book where the customer only pays for shipping or a buy-one-get-one-free discount. This stage is essential for converting interest into initial transactions within your value ladder strategy.
- Middle — By now, you have provided substantial free value. It’s time for customers to make a more significant commitment. This middle stage should feature your core offerings, whether it’s a subscription service, a primary product, or a main service. The goal is to deepen the relationship and investment with your customers through a well-structured ladder pricing strategy.
- Back End — This stage targets your most dedicated customers, those who have progressed through the earlier stages and are highly engaged with your products or services. Here, you offer more expensive, high-value items. This could be advanced training programs, comprehensive service packages, or exclusive memberships. The back end is crucial for maximising the revenue potential of your value ladder strategy.
- The Peak — At the top of your value ladder is your premier offer. This is where you provide the most value for the highest price. It’s designed for your most loyal customers who seek the ultimate transformation or solution your business can provide. This could be one-on-one coaching, a comprehensive consultancy package, or an all-inclusive service offering. This peak offer is the culmination of your value ladder strategy, representing the pinnacle of your customer value journey.
Our Tactical Recommendations
One highly actionable tactic is creating micro-moments along the buyer’s journey. These small but meaningful interactions nudge prospects forward, making each rung of the value ladder feel like a natural progression. Clients often discover that using ABM strategies to focus on high-value accounts can accelerate their movement to higher tiers. Additionally, regularly revisiting the ICP ensures that your offerings evolve as customers move through the ladder—this keeps the experience relevant and impactful for clients at every stage.Get In Touch
Questions to Ask Yourself Before Creating Your Value Ladder
- What does the prison state look, sound, and feel like? Understand the current pain points and challenges your prospects face. This insight will help you craft offers that address their specific needs at each stage of the value ladder.
- What does the paradise state look, sound, and feel like? Envision the ideal outcome for your customers after they have progressed through your value ladder. Knowing this helps in designing offers that guide them towards this ultimate goal.
- What is your process to get clients from one side to the other? Clearly outline the steps and transitions you will use to move customers from their initial state to their desired state. This involves mapping out each stage of the value ladder and ensuring smooth transitions.
- Can you break your products up into blocks? Consider if your offerings can be modularised into smaller, more manageable components. This can make it easier to provide incremental value and upsell customers to higher tiers within your value ladder.
- Can you add new products? Think about potential new products or services that could fit into your value ladder. Continuously innovating and adding value can keep your ladder dynamic and appealing.
- Think about ways that you can upsell. Identify opportunities for upselling at each stage of the value ladder. This could involve offering premium versions of your existing products, bundling additional services, or providing exclusive benefits for higher-tier customers.
Step-by-Step Methodology
- Know Your Target Market
Before constructing an effective value ladder, you must gain an in-depth understanding of your target market. This foundational step ensures your offers resonate and provide genuine value.
Consider the following questions to define your target audience:
- How old are they?
- What is their annual income?
- What are their primary concerns and stressors?
- What excites them?
- Which influencers do they follow on social media platforms like Facebook or Instagram?
- What publications do they read?
A precise understanding of your dream customers makes it easier to craft compelling offers for your value ladder strategy.
- Outline Your Offers
Once you have a clear picture of your target market, the next step is to outline the offers for your value ladder strategy.
If you already have an established business, list your current offerings and brainstorm potential future products or services. For new businesses, this stage involves identifying the problems your target market faces and envisioning solutions to address these issues.
Organise these offers into a ladder pricing strategy based on their value and price. Here’s an example structure:
- Tier 1: Free eBook — “How to Start a Freelance Writing Business”
- Tier 2: Course on Finding Clients (£57)
- Tier 3: Course on Increasing Your Rates (£199)
- Tier 4: One-on-One Coaching (£2,000)
- Choose a Starting Point
There are two paths to consider here:
- For Existing Businesses: After outlining your value ladder, decide on the next offer to develop. This could mean scaling your highest offer—ideally reaching £1 million in revenue before expanding your macro value ladder—or adding a new tier to your existing ladder.
- For New Businesses: Choose a starting point, typically in the middle or front-end of your value ladder. Opt for something like a £20 – £90 course or eBook to generate initial revenue without being too challenging to sell.
- Build a Sales Funnel
Select from these three high-converting sales funnels to facilitate your value ladder strategy:
- Tripwire Funnel: Ideal for selling front-end products to cold traffic (e.g., via Facebook ads). This funnel uses a free bait to attract prospects, captures their payment and shipping information, and then upsells them with an attractive one-time offer.
- Webinar Funnel: Effective for selling moderately expensive products, services, or courses. This funnel allows you to build trust, educate your target market, and sell your offerings through a live or recorded webinar.
- Application Funnel: Suitable for pre-qualifying leads for coaching, consulting, or freelancing services. This funnel requires prospects to provide information before scheduling a call, ensuring high-quality leads.
By meticulously implementing these steps, you can create a robust value ladder strategy that attracts, engages, and retains customers, maximising their lifetime value through a structured ladder pricing strategy. This approach ensures each stage of your value ladder is strategically crafted to provide increasing value, fostering long-term loyalty and driving sustainable business growth.
Best Practices for Your Value Ladder Strategy
The Down-Sell Offer
Unlike upsell offers, which are presented as customers move up your value ladder, down-sell offers are targeted at those who have decided not to proceed further. Marketing experts suggest providing a lower-cost alternative to retain these customers.
For instance, if a customer reaches the fourth step of your value ladder but opts not to continue, you can offer the same product at a reduced price with fewer features. This approach helps ensure you don’t lose the customer entirely and can still generate revenue.
The Cross-Sell Offer
Cross-selling occurs when a lead or client has just made a purchase or is about to purchase your core offer. This strategy increases revenue by encouraging customers to buy related or complementary items, thus enhancing their overall experience and satisfaction.
For example, if you sell computers, you might offer an external hard drive or protective case to a customer who has just bought a laptop. This not only boosts sales but also shows customers that you care about their needs beyond the initial transaction.
One-Time Offer
A one-time offer is a tactic used to create urgency and increase the likelihood of conversion. Typically, this involves combining your core offer with additional freebies or discounts for a limited time.
One-time offers can include valuable physical items, digital downloads, access codes, or discount coupons. These offers are presented strategically during the sales process, whether as part of a cross-sell or down-sell, to enhance the attractiveness of your value ladder strategy and encourage immediate action.
What common mistakes should I avoid with my value ladder strategy?
Discount Default
Procurement departments frequently assert that suppliers are too expensive, expecting that the initial reaction will be a price reduction. Escaping the discount default mentality requires a shift in approach. As a sales agent, it’s crucial to have the confidence to face a prospect and assert, “No, we are not too expensive; in fact, we’re probably not charging enough for the value we deliver.”
Building this confidence hinges on effectively communicating your value. Without this ability, the tendency to resort to discounting becomes almost inevitable.
Believing Your Product is a Commodity
Customers are not merely purchasing your product; they are buying the entire experience that comes with it. The product itself is just one element. If you cannot differentiate through the product alone, consider how you can stand out in other areas of your business.
Every team member within your organisation contributes to the overall customer experience, whether through service delivery, support, or onboarding. It is essential to recognise and enhance these contributions to add value beyond the product itself.
Focusing on Presenting Your Product Before Understanding the Customer
Too often, sales calls begin with the seller immediately diving into a presentation about their product, neglecting to understand the customer’s needs first. Many organisations label their offerings as solutions. However, a solution must address a specific problem.
If you don’t understand the customer’s problem, you cannot offer a true solution. Therefore, it is vital to prioritise understanding the customer’s challenges before presenting how your product or service can resolve them.







