Selecting the right CRM model can feel like navigating a maze, especially with so many options promising to revolutionise your customer relationships. But what if the key to mastering customer management lies not just in choosing a model but in understanding the unique frameworks behind them? Imagine knowing exactly how the IDIC model, the QCI model, or Payne’s five-process model could be the game-changer your business needs.
You’re about to discover how these models aren’t just theoretical concepts but powerful tools that, when strategically applied, can transform your CRM approach. Ready to explore how to turn these blueprints into actionable strategies that drive real results? Let’s dive in and unlock the potential of these CRM frameworks.
- Choose the Right Model: Understanding the unique strengths of each CRM model, such as IDIC and QCI, allows you to align your customer management strategy with your business goals effectively.
- Strategic Implementation: Applying these CRM models isn’t just about following a framework; it’s about strategically integrating them into your existing processes to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Customised Solutions: Not all CRM models fit every business—learn how to customise the chosen model to meet your specific customer relationship needs.
What key concepts should I consider when implementing a CRM model?
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is a strategy employed by companies to manage interactions with current and potential customers. CRM systems help organisations streamline processes, build customer relationships, increase sales, enhance customer service, and boost profitability.
When we discuss CRM, we often refer to a CRM system. This tool is pivotal for contact management, sales management, agent productivity, and more. The primary objective of a CRM system is straightforward: to improve business relationships and facilitate business growth. CRM tools assist in managing customer relationships throughout the entire customer lifecycle, covering every marketing, sales, e-commerce, and customer service interaction.
What Matters Most?
From our experience, a CRM model must be the backbone of your digital transformation, seamlessly integrating with other systems to provide a unified view of the customer journey. Clients often discover that flexibility is key, as the CRM model needs to adapt to evolving customer expectations and technological changes to stay relevant. Typically, the most successful CRM models incorporate customer feedback loops, continuously refining processes based on real-time insights, which not only improve the system but also deepen customer loyalty and engagement.Get In Touch
CRM models can significantly enhance your understanding of how your company reaches, converts, and retains customers. A CRM model dictates your company’s strategies for customer acquisition and retention. The most popular CRM models guide your team on learning about customers, segmenting them, contacting them, and refining your approach. CRM software bolsters the adherence to CRM models by improving your company’s practices around customer data, relationships, and sales.
In addressing the myriad challenges associated with sales work, companies across various industries have increasingly adopted CRM software with notable success. One report indicates that 65% of companies using mobile CRM are meeting their sales quotas. This success is often attributed to the implementation of a CRM model alongside the software. Below, we explore how CRM models and software synergise to make sales work more manageable.
A CRM model is a structured workflow that directs all interactions your team has with leads, prospects, and customers. It provides a flexible framework that your company can utilise to acquire and retain customers. It’s important to note that a CRM model differs from CRM software; the latter enables you to navigate your CRM model more efficiently while ensuring seamless coordination within your team.
How do the IDIC, QCI, and Payne’s models enhance customer relationships?
Understanding the different types of CRM models is crucial for businesses aiming to optimise their customer relationship management strategies. Here, we delve into four of the most prevalent CRM models: the IDIC model, the QCI model, Payne’s Five Process Model, and the CRM Value Chain. Each of these models provides unique frameworks to help businesses acquire, retain, and manage customer relationships effectively.

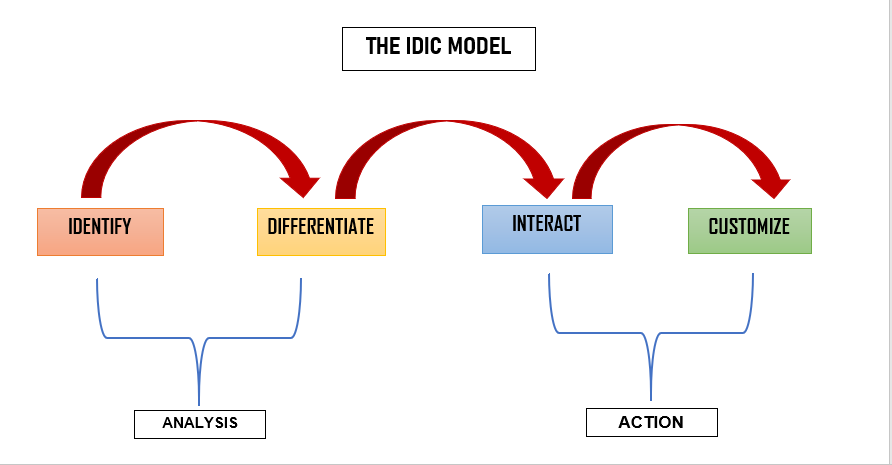
IDIC Model
Developed by the Peppers and Rogers Group, the IDIC model serves as a comprehensive blueprint for implementing CRM in various scenarios. IDIC stands for Identify, Differentiate, Interact, and Customise.
Identify The initial step involves gathering extensive information about your customers, such as their names, addresses, and purchase histories. This data collection occurs at every point of contact across the company, aiming to gain a deep understanding of customers’ needs, wants, and purchase behaviours.
Differentiate Next, segment your customers based on their current and projected lifetime value. Not all customers hold the same value to the business; therefore, prioritising efforts towards the most valuable segments optimises profitability. Tailor your interactions to suit each segment for maximum effectiveness.
Interact In this stage, apply your CRM plans to interact with your customers. After analysing and categorising customers, develop customised interactions. For instance, offering loyalty benefits to valued customers can foster retention and encourage continued spending. Learn from each interaction to enhance future engagements continuously.
Customise Finally, after documenting interactions, analyse them to develop more personalised one-to-one services. The objective is to meet individual customer needs and expectations precisely.
Challenges and Solutions in Adopting the IDIC Model
Adopting the IDIC model can be challenging, particularly in integrating disparate data sources. Advanced data integration tools can consolidate various data formats into a unified customer view. Regular training programmes ensure staff can effectively utilise customer data. Data privacy and security are critical; robust governance policies are essential to handle customer information responsibly. Continuous monitoring and adaptation keep the IDIC model aligned with evolving customer expectations, ensuring it remains effective and relevant.
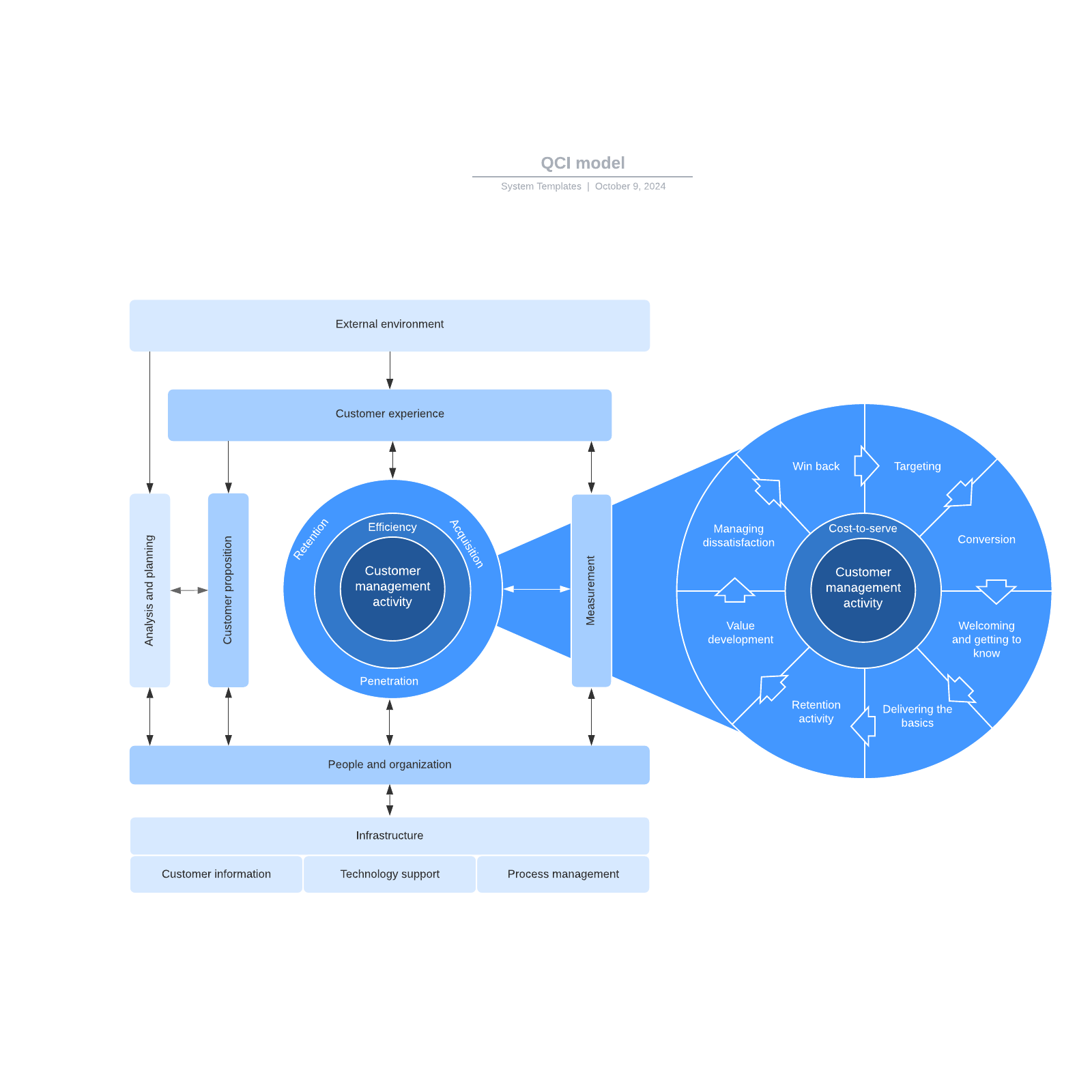
QCI Model
The Quality Competitive Index (QCI) model, often referred to as a customer management model, focuses on three core activities: acquisition, retention, and penetration.
The QCI model begins by examining the customer’s external environment—their pain points, business goals, and other factors that influence their readiness to engage with your sales team. This understanding impacts the overall customer experience, which in turn shapes your customer proposition and management activities. As illustrated by the inner circle of the QCI model, numerous activities are essential for acquiring and retaining customers.
Crucially, the QCI model also considers the integral role of people and technology in maintaining this system. Although the term “relationship” has been replaced in this model, it still fundamentally revolves around human interactions.
Payne’s Five Process Model
Developed by Adrian Payne and Pennie Frow, Payne’s Five Process Model adopts a cross-functional approach to effective CRM processes. This model is structured around five key processes and four essential elements of CRM implementation.
Five Key Processes:
- Strategy Development: Define clear CRM objectives that align with your business goals. Conduct a comprehensive market analysis to understand customer needs and preferences, laying the groundwork for a targeted CRM strategy.
- Value Creation: Identify unique value propositions that differentiate your offerings. Develop detailed customer personas and journey maps to tailor your value creation efforts. This step focuses on understanding what truly matters to your customers and how your business can meet those needs uniquely.
- Multichannel Integration: Ensure a consistent customer experience across all channels, from digital platforms to in-person interactions. Utilise technology to create a cohesive communication strategy that keeps customers engaged and informed.
- Information Management: Implement robust data management systems to capture and analyse customer data. Use this data to personalise customer interactions and make informed strategic decisions. This step is crucial for understanding customer behaviour and preferences.
- Performance Assessment: Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of your CRM processes to ensure continuous improvement.
Four Essential Elements for Successful CRM Implementation:
- CRM Readiness: Conduct a readiness assessment to determine how prepared your organisation is to implement a new CRM process.
- CRM Change Management: Since CRM implementation involves significant cultural and operational shifts, invest in change management to support the transition.
- CRM Project Management: Effective project management is necessary to handle the complexities of CRM initiatives as they grow.
- Employee Management: Employee buy-in is crucial for successful CRM. Ensure your employees understand the strategies and processes and are fully engaged with the new customer-centric culture.
Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing Payne’s Five Process Model
- Initiating Strategy Development: Start by defining clear CRM objectives that align with your business goals. Conduct thorough market analysis to understand customer needs and preferences, setting the foundation for a targeted CRM strategy.
- Embracing Value Creation: Identify unique value propositions that set your offerings apart. Develop customer personas and journey maps to tailor your value creation efforts. This step is about understanding what truly matters to your customers and how your business can meet those needs uniquely.
- Integrating Multiple Channels: Ensure consistency in customer experience across all channels, from digital platforms to in-person interactions. Utilise technology to create a cohesive communication strategy that keeps customers engaged and informed.
- Managing Information Effectively: Implement robust data management systems to capture and analyse customer data. Use this data to personalise customer interactions and make informed strategic decisions. This step is crucial for understanding customer behaviour and preferences.
- Assessing Performance: Continuously evaluate your CRM processes to ensure they remain effective and aligned with your business goals.
Adhering to these steps and elements ensures a comprehensive approach to CRM implementation, driving effective customer relationship management and fostering business growth.
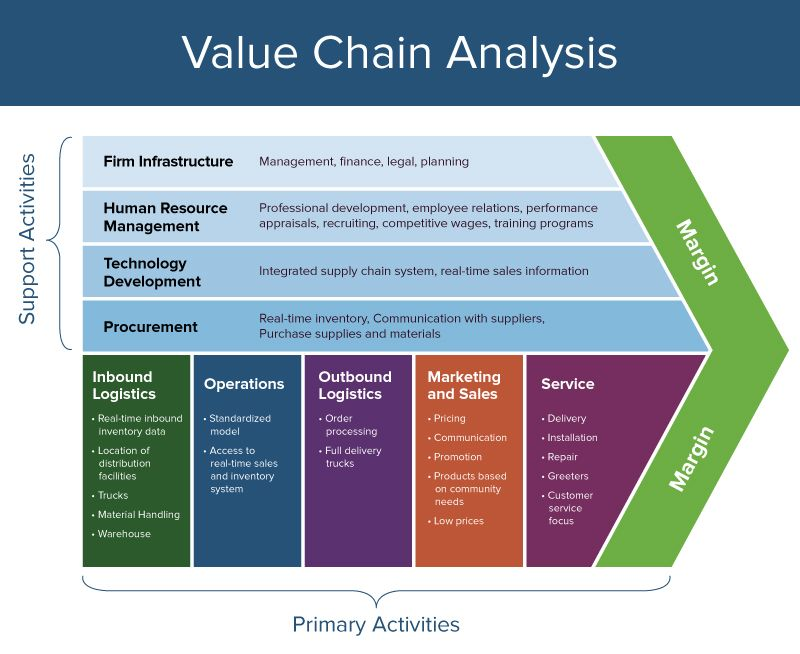
CRM Value Chain
The CRM value chain is a sophisticated model developed by Michael Porter, designed to identify and prioritise the processes a business uses to create an end product or service for its customers. The primary objective of the value chain model is to pinpoint the most valuable activities within a company and refine these processes to secure a competitive edge.
Applying this principle to customer relationships, the CRM value chain examines all stages and activities required to build and maintain a relationship with a customer. This CRM model is divided into two key stages: primary and support.
Primary Stage
The primary stage of the CRM value chain consists of five essential processes that underpin the strategy.
- Customer Portfolio Analysis: Similar to the IDIC model, the first step involves analysing your customer base to identify your SSCs (Strategically Significant Customers) – those who generate the most value for your company. This analysis helps businesses understand their customers’ needs and expectations, enabling the development of strategies to maximise their lifetime value.
- Customer Intimacy: The next step is to foster closer engagement with customers by building on the existing database of information. At each touchpoint, data should be collected to enhance understanding and service delivery. The better you know your customer and adjust your service accordingly, the more likely you are to retain their business over the long term.
- Network Development: A business’s network encompasses all individuals and entities involved in the value chain, including partners, suppliers, customer service teams, investors, and more. The goal is to utilise customer data to inform processes at every network level, ensuring that the entire system collaborates to optimise the customer experience.
- Value Proposition Development: With comprehensive customer information and interaction data at hand, businesses can create significant value for their target customers. This process involves shifting the focus from the product to the service, aiming to reduce process costs and increase value for the customer.
- Relationship Management: The final stage of the primary process is managing the customer lifecycle. This involves continuously evaluating and refining business processes and organisational structures to effectively manage customer acquisition, retention, and development.
Support Stage
To implement the strategic processes of the primary stage effectively, five supporting conditions are necessary:
- Leadership and Culture: Strong leadership and a customer-centric culture are crucial for fostering an environment where CRM strategies can thrive.
- Procurement Processes: Efficient procurement processes ensure that the necessary resources are available to support CRM activities.
- HR Management Processes: Human resources play a pivotal role in managing and deploying the right talent to execute CRM strategies effectively.
- IT/Data Management Processes: Robust IT and data management systems are essential for capturing, storing, and analysing customer data to inform strategic decisions.
- Organisation Design: An organisation’s design should facilitate seamless integration and execution of CRM strategies across all departments.
Developing these underlying conditions will support a successful CRM value chain implementation, enabling businesses to enhance their customer relationship management and secure a competitive advantage in the market.
Our Tactical Recommendations
We’ve found that implementing AI-driven analytics within your CRM model is essential for anticipating customer needs and personalising interactions, which often leads to higher satisfaction and conversions. Clients frequently enhance their CRM’s effectiveness by ensuring it supports mobile access, enabling teams to engage with customers and update data on the go. From our experience, integrating retention strategies directly into the CRM model allows businesses to identify at-risk customers early and take targeted actions to reduce churn, thereby maximising customer lifetime value.Get In Touch
How can a CRM tool improve customer relationship management strategies?
Managing customer relationships is no simple task. Not only do you need to meet customer expectations, but you also strive to exceed them, fostering long-term loyalty and retention. Achieving this requires organising contact information, data, and customer queries in a manner that is easily accessible for every customer interaction. A CRM tool simplifies this complex management process.
Here are several ways you can leverage a CRM tool to support your CRM model:
- Organise Customer Information: A CRM tool allows sales representatives to record customer calls, track emails, and automatically update customer records. This information can be referred to at any time, such as before customer check-in calls, ensuring that customer interactions are personalised and the customer feels valued.
- Easily Access Data: Valuable customer data is readily available within your CRM, providing insights about each customer and enabling you to personalise your value propositions. Data is automatically integrated into sales reports, allowing you to track metrics such as response time and call outcomes. Furthermore, if you utilise a mobile CRM, your representatives can access this data while visiting customers, ensuring they are well-prepared for every interaction.
- Integrate with Marketing and Support: CRM tools can integrate with marketing automation software and support platforms, ensuring consistent communication across all channels and departments. This integration prevents any communication gaps, ensuring that each department understands customer needs and the steps being taken to meet those needs.
For instance, the marketing team can see what top customers are asking from sales and support. They can then use this information to create helpful resources such as whitepapers, blog posts, and reports tailored to these customers’ needs.
By using a CRM tool effectively, you can enhance your CRM model’s implementation, ensuring your business processes are streamlined and customer interactions are optimised. This strategic approach not only improves customer satisfaction but also drives business growth and efficiency.









